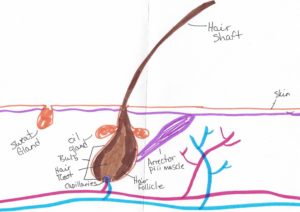
Skin 101 [Show Notes]

Skin 101
Your skin is the largest organ of your body.
It has 3 jobs: Protection, Regulation, Sensation
Natural complexions are being viewed as more beautiful than a “tan”.
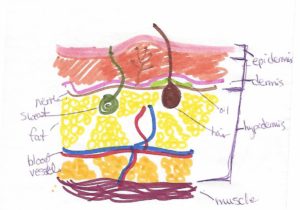
3 Layers
- Epidermis (above skin) – waterproof, gives you your color, the layer we see
- Dermis-Epidermis junction – a protein layer containing collagen and elastin to give skin flexibility and stretchability
- Dermis – where your glands, hair follicles, and nerves are
- Hypodermis – (below skin) – houses adipose tissue for insulation, and blood vessels
The Epidermis is made up of several separate layers based on what is happening in the cell’s lifetime.
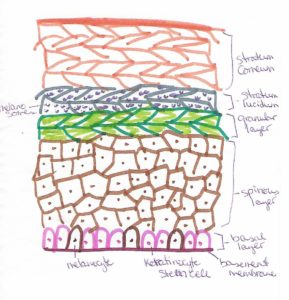
The basement membrane sits right on top of the Dermis-Epidermis junction, made up of fibrous proteins to be a solid foundation.
Epidermis Layers
- Basal Layer – Keratinocytes (makes Keratin) and Melanocytes (makes Melanin) – stem cells.
- Spinous Layer – Cells are actively dividing and getting squished together
- Granular Layer – Cells start making the proteins (keratin or melanin) that they are coded to make and it fills up all the intracellular space; the organelles of the cells get crowded out
- Lucid Layer (Clear) – Keratinized cells are clear; Melanin-filled cells are colored. Cells are officially dead. Cells become coated in a hydrophobic (afraid of water) oil.
- Hard Layer – cells are tightly packed together and dry; the layer we can touch.
These cells are being continuously produced and shed off and replenished because the skin takes a lot of abuse.
Deeper Stuff
UV light from sun or tanning beds (heaven forbid!) stimulates melanocytes to divide faster and create more melanin (because melanin is reflective and keeps UV rays away from the important cells). This is how a tan is created. But during times of huge exposure, like tanning beds, there’s not enough melanin to keep all the UV rays out so those rays can wreak havoc on the collagen and elastin proteins. This is why over-tanned skin ages faster.
Hydrating makes sure that the living and dividing cells are plump and as healthy as possible so when they move to the next layer, they are well nourished.
Protection: keeps dirt and bacteria out; protections from UV radiation
Regulation: releases sweat to cool the body’s temp; subtly moves blood vessel closer or farther away from the surface to either cool the warm blood (like after exercise) or keep it warm (like in the winter).
Sensations: allows you to feel things that touch you or come close to you.
I can’t seem to find any free footage of the original episode (Season 1, Episode 3) without having to sign up for a free streaming service. The Mythbusters did a “revisit” of their Goldfinger episode. Netflix the original, if you can.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/