Basics
Brain lesion = a group of brain cells that look different from surrounding cells on a brain scan
Dark lesions – an area where the brain cells are missing or an area where signal is not firing (damaged cells)
Light lesions – an area where the signals are firing at the wrong times (like a shorted out wire). Seizure – when the brain fires the electricity at the wrong time.
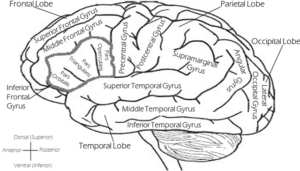
Lesions around the brain
A lesion in the Parietal lobe could affect how the body translates sensations (i.e. pain). These lesions are usually caused by injury or stroke.
If there is a lesion in the optical lobe of the brain (the area that “sees” what your eyes are looking at), then the signals from the eyes may not come through, and therefore the parietal cannot help map what you were looking at once it’s not there anymore.
Sensory seizures – feeling things on you or touching you that aren’t really there. (unsure if this is related to the auras that come before migraines). No medication necessary.
Extinction phenomenon: thinking that a sensation stopped before it really did. You body can’t translate two messages of the same type at the same time. Like when you try to locate the same place on each side of your body (i.e. making pigtails even).
Some Big Words
Dyslexia: can be related to written language, spoken language, or any other message being translated as language
Dysphasia or Aphasia: mixed up or missing words
Dyscalculia: it’s hard to math. Difficulty estimating distances, spacial mapping, and time passage. Dana White of A Slob Comes Clean talks about TPAD (Time Passage Awareness Disorder)
Apraxia: unable plan what you want your body to do in order to make your body do it. The deeper the path the more “natural” the action is. Muscle memory is just an extremely well-developed motor path, so that you can even not do that action for a while, and when you do it again, you don’t have to “relearn” it. If this is caused by a stroke, therapy can help try and re-route the information. Apraxia can affect gross motor movements (large movements with your body) – aka global apraxia, or it can affect speech motor planning.
Gerstmann Syndrome: no motor path to write, or math, or to feel and use your fingers as separate digits. Also involves a left-right mix up. In adults, it’s the results of a stroke. In kids, they have not a clue. Therapy can help kids get past the motor issues, but not the mathing issues.
Constructional apraxia: know how blocks should fit together, but the brain can’t make their body build it.
Dressing apraxia: know how clothes should be worn and where it goes, but the brain can’t make the body dress itself. This shows up in dementia and Alzheimer’s a lot.
Amorphosynthesis – your brain is not aware of some part of your body. Usually a symptom after as stroke.
Another symptom of a stroke is when a person is unaware of one-half of their visual field. So they will only write on one half of the paper (the half they can see) or read only one half of the page of a book.
Anosognosia – a person is not aware that they have a disorder, disease, or disability. This is not just denial. The area of their brain that would recognize “I’m sick” or “I’m hurt” doesn’t work.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Like the Facebook page
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/