Voice Troubles – Episode 117
Laryngitis
Laryngitis, known as inflammation of the larynx, is the most common cause of hoarseness and voice loss. It is very common in viral infections, such as a cold, flu, or adenovirus. Acute laryngitis is caused by an illness, while chronic laryngitis may be a secondary symptom of another problem like acid reflux, smoking, or severe thrush.
There is a lot of advice that goes around about what can “cure” laryngitis or get rid of hoarseness. Hydration is always key. Some of the other advice is more anecdotal. But above all, whatever you do for a hoarse voice, DO NOT WHISPER!
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease (LPRD)
LRPD is a condition where stomach acid refluxes into and burns the vocal cords. It may or may not accompany GERD. It causes intermittent to chronic hoarseness, swallowing troubles, throat pain, or a constant sensation that something is stuck in your throat.
Misuse and Overuse
Misuse of your voice is defined as the inefficient use of your voice. It may stem from poor posture, poor breath support, or poor hydration. Overuse of your voice is defined as excessively loud or prolonged use of your voice.
Lesions
Vocal cord lesions are benign growths on the vocal cords that interfere with normal vibration. These can result from repeatedly prolonged periods of misuse or overuse. They will cause chronic hoarseness or sporadic voice-silencing. They come in three varieties and are all treatable: nodules, polyps, and cysts.
Nodules require vocal rest and voice therapy and training to help make sure they don’t happen again. Polyps and cysts require micro-surgery where the growth is removed, and then rest and therapy and training will follow.
Hemorrhage
If you have a sudden loss of voice after yelling, then it is possible a hemorrhage occurred. A hemorrhage is when blood vessels in the surface of the vocal cord burst and fill it with blood. COMPLETE REST is required until the blood is reabsorbed by the body.
Paresis and Paralysis
Paresis is the fancy word for weakness. Vocal weakness can occur during a viral infection or after neck or throat surgery. It can be temporary and strength will return on its own after a recovery period, or it can be permanent. Prolonged or permanent vocal weakness can be improved somewhat through therapy and training.
Paralysis, on the other hand, is neurologically based, whether damage happened in the area of the brain that controls the voice and supporting structures, or the nerves in and around the larynx are damaged. This can also be temporary or permanent and is generally one-sided.
Symptoms of a weakened or paralyzed vocal cord include noisy breathing – like something is hanging in the way of the air flow. And breathy talking – like when someone is trying to use their “sexy” voice and there’s more air making noise than vocal vibrations. There is a surgical repair process that involves taking the working vocal fold and stretching it over so when it activates, it will still come in contact with the unmoving vocal fold.
Callbacks
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Voice – Episode 116
Voice Anatomy
Larynx: a structure on top of the trachea (windpipe) and holds the vocal folds
Vocal Folds: also known as vocal cords; the soft tissue that vibrates and creates sound when air passes through them. There’s one on each side.
Vocal Box: the structure that surrounds the vocal cords. It’s made of 3 parts – a cover that is made of epithelial cells (similar to the inside of your mouth), vocal ligaments that hold it all in place, and the thyroarytenoid muscle that is responsible for relaxing the vocal cords into place.
Glottis: the opening in the middle of the vocal folds where they sperate for breathing and closes for talking and swallowing.
Voice Production
There are 3 levels of sound production to equal talking.
- Voiced Sound: this is the basic vibration of the vocal cords and creates a “buzzing” sound. This is the first step of babies learning to talk and communicate. We say the baby is “discovering their voice.”
- Resonance: the “buzzing” sounds are amplified by resonating chambers that include the throat, mouth, and nasal cavity. The sound produced by these chambers is what give you your distinct voice. To produce sound without using one or more of these resonating areas alters your voice significantly.
- Articulation: movement of the tongue, soft palate, lips, and jaw modifies and changes the sound to produce words and intelligible speech.
Singing
Singing adds the breathing system to regulate the air pressure that vibrates the vocal cords. The rhythm of putting words to music to create singing changes the pattern and length of words and syllables, and the strength of the diaphragm plays a big part in that.
Just like guitar strings, the tighter the vocal cords, the higher the pitch. More relaxed vocal cords produce a lower pitch. *If you listened to this episode, I’m so sorry for your ears!*
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Gag Reflex – Episode 115
Gag Reflex Basics
The official name of your gag reflex is the pharyngeal reflex or laryngeal spasm. Trigger points for the gag reflex can be found on the roof of the mouth, back of the tongue, in the tonsil area, the uvula, and the back of the throat. The purpose of this reflex is to prevent objects from entering the throat that did not first progress through the normal swallowing process. It also helps prevent choking.
Gag Reflex Progress
When the reflex is triggered, the soft palate raises to close off the nasal passage. Then the pharyngeal muscles contract on both sides to try and force whatever made it too far down back up into the mouth. If the input is strong enough, it can also trigger vomiting (this is how vomiting is induced in eating disorders such a bulimia).
Do you Gag?
One in three people lacks a gag reflex, which means rather large things can enter their throats without triggering a reflex. This is possibly how sword-swallowing got its start.
The other side of this coin is someone with a hypersensitive gag. They can have trouble swallowing large pills and large bites of food. Dentist visits and even neckties can trigger this unpleasant reflex. It can be a part of a larger issue, such as Sensory Processing Disorder or Autism. Or it can be a preconditioned issue due to a previous experience. In either case, speech or occupational therapy can be done and will include desensitizing areas of the mouth to touch.
Other Protective Reflexes
- The Reflexive Pharyngeal Swallow is a triggered swallow that clears the pharynx of residue. The glottis will close and allow the pharynx to move stuff to the digestive tract. This is a protective mechanism to keep stuff out of the airways.
- Phayngoglottal Closure Reflex happens when the glottis closes inside the larynx without the continuation of a swallow.
- Phango-Upper Esophageal Sphincter Contractile Reflex occurs during any type of reflux from the stomach. While some stomach contents may make it past the lower esophageal sphincter, so the upper one prevents it reaching into the throat and mouth.
Bottom Line
All of these reflexes are protective to prevent choking or improper ingesting of things. They can be damaged to different degrees during head trauma or stroke. But surprisingly, smoking causes the most damage to the protective reflexes on the pharynx.
Callbacks
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Bad Breath – Episode 114
Bad Breath Basics
Halitosis, aka bad breath, can have many causes. Some bad breath you can prevent with the choices you make, but some bad breath can be a sign of a more serious issue or disease.
Oral Health
You should brush your teeth for at least 2 minutes twice a day, including the surface of your tongue, then rinse your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash. Follow one of your brushing sessions with a good flossing. This allows you to get any food debris and bacteria build-up out of the way on a daily basis.
You should see your dentist twice a year for a deep cleaning and a check-up on your overall oral health. Your dentist will be able to help you with bad breath issues that may stem from more complicated issues like cavities, gum disease, poorly-fitting dentures, or thrush.
Dry mouth, whether due to your natural biology, medication side effects, or mouth-breathing, can lead to bad breath due to the imbalance of bacteria growth.
Your Choices
Smoking and other tobacco products can make your breath smell bad even when you are not actively using it.
The foods you eat also affect the status of your breath. The compounds that cause eaten and digested foods to smell contain sulfur-based compounds. These include broccoli, cabbage, brussel sprouts, onions and garlic, coffee, and fish. The funny thing about these smelly compounds is that they can actually make your WHOLE BODY smell (including your breath as well as other exiting air) until they have passed all the way out of your body!
Diseases
Infections, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinusitis, can lead to distinctive bad breath. Postnasal drip can lead to bad breath as well. Pharyngeal diverticula that trap old food bits can make your breath smell, as well as tonsil stones that are calcified debris trapped by the tonsils. Bad breath can also be indicative of acid reflux or GERD.
Certain diseases that have telltale breath smells include diabetes, liver disease, and kidney disease.
People with diabetes are at risk of a medical emergency known as Diabetic Ketoacidosis, in which a lack of insulin renders the body’s cells unable to use the available sugar. The body starts burning fatty acids for energy and the waste product is ketones. Ketones cause the body to become very acidic. This leads to a rapid transfer of water (extracellular fluid rushes into the blood to try and neutralize and dilute the ketones and then the kidneys rapidly try to flush out the acidic fluid through the urine) which can lead to fatal dehydration. Clinicians are taught that people experiencing ketoacidosis may have fruity-smelling breath or breath that smells like acetone or nail polish remover.
People with liver disease may have breath that smells musty or like a mildewing basement. And people with kidney disease may have breath that smells fishy or like urine or ammonia. Ammonia is a typical by-product that is released in urine. Someone with kidney disease may not be able to filter out the ammonia compounds effectively. Therefore, the ammonia compounds will circulate in the blood.
Call Back
Brush your tongue – Tastebuds
Tonsil stones – Tonsils
Pharyngeal diverticula – Dysphagia
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Dysphagia – Episode 113
Dysphagia Basics
Having difficulty swallowing or the inability to swallow is known as dysphagia.
Symptoms of dysphagia include:
- Pain while swallowing
- The sensation of food stuck in the throat or chest
- Drooling
- Hoarseness
- Regurgitation
- Reflux
- Unexpected weight loss
- Choking, coughing, or gagging when swallowing
- Taking tiny bites
Dysphagia by Phase
There are several conditions that can affect each phase of the swallowing process.
Oral Phase
Dysphagia during the oral phase, or voluntary phase, can be caused by neurological conditions like Multiple Sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy, advanced Parkinson’s. Brain damage caused by trauma or stroke can also cause trouble swallowing in adults.
Dysphagia in Kids
Babies start out nursing or feeding through a bottle and their swallowing mechanism is reversed. A reverse swallow is when the tongue is thrust forward or out of the mouth to open the throat and allow food or drink down the esophagus. As children learn to eat solid food and drink from a cup, the swallowing procedure changes. Children can also have trouble swallowing, but the root causes are completely different. Premature birth, low birth weight, cleft lip or palate, and tongue or lip ties can lead to swallowing issues if not corrected with therapy. These issues can cause swallowing issues with the reverse mechanism as well as make it difficult to convert to a regular swallow. Children with low muscle tone are also more likely to stick with the reverse swallow because it is easier.
Pharyngeal Phase
Pharyngeal diverticula are pouches that form in the mucous membrane above the esophagus. These pouches can collect food particles that don’t get swallowed. This can cause bad breath, as well as coughing, and constant throat-clearing because it feels like something is stuck in the throat.
Esophageal Phase
There are several swallowing issues that stem from the esophagus and esophageal phase.
- Achalasia is an issue where the sphincter that opens into the stomach doesn’t relax to allow food to pass through. This can cause pressure in the chest and may possibly lead to regurgitation if it persists.
- Diffuse spasms happen when the peristalsis rhythm of the esophagus muscles is poorly coordinated.
- Stricture is also known as a narrowed esophagus. It can be a result of injury and scarring from GERD.
- An esophageal ring is when a thin area of the lower esophagus is narrowed. This is also a result of scar tissue from chronic GERD. The scar tissue from acid damage tends to be less flexible which can cause pain.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis is the overpopulation of eosinophils in the esophageal lining due to food allergies. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cells that show up in very specific situations – parasitic infections, cancer, or allergies.
Dysphagia Risk
The risk of dysphagia increases with age, mostly because the risk of the conditions that cause dysphagia increases with age as well. And while dysphagia can be very uncomfortable, the biggest concern is with the risk of aspiration, or breathing food or drink into the lungs, that leads to pneumonia.
Call Back
Swallowing
Muscle Tone discussion – Accordion in Your Brain
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Swallowing – Episode 112

The 3 Phases of Swallowing
Oral Phase
This phase includes chewing and saliva mixing with the food to form a bolus (a little glob of mashed up food). Then the tongue moves the bolus towards the back of the mouth. The tongue starts by pressing against the hard palate behind the front teeth. Then the sides of the tongue raise up to also press against the hard palate inside the teeth. At this point, the bolus has nowhere to go except towards the back of the throat.
Pharyngeal Phase
The vocal folds in the larynx close to keep food out. The larynx also moves up as the epiglottis covers it to seal off the airway. Then the soft palate and uvula move up and close off the nasal passage So now there is only one way out.
Esophageal Phase
The bolus moves into the esophagus (because it is the only open path). The esophageal muscles contract from top to bottom (this waving, rhythmic muscle movement is called peristalsis) to push the bolus into the stomach.
Swallowing Reflex
There are sensory receptors in the pharynx and tongue that receive touch signals. When they are touched by a bolus, the signals are sent to the brain stem and the return signal results in involuntary and automatic movements of the larynx and epiglottis. This is a good thing since swallowing is a very rhythmic process and you want food and drink to continue going in the correct direction.
This reflex cannot be triggered by sticking your finger in your throat. You are more likely to trigger a gag reflex that way. The voluntary steps of swallowing must be initiated before the involuntary portion of the process takes over.
Weird Swallowing Scenarios
How do you swallow with your mouth open?
At the dentist, you are usually laying in the chair on your back and facing the ceiling. There are at least three tools and two hands in your mouth. Things in your mouth trigger saliva production. Also, generally one of the tools the dentist is using is emitting water. The natural reflex when you have to hold your mouth open for a long time is to bring the back of the tongue and the soft palate together. This seals off the throat and allows you to still breathe through your nose. The liquid in your mouth plus gravity creates a puddle at the seal of your tongue and soft palate. Because the touch sensors to trigger your swallowing reflex are also in this area, it is likely you begin to panic because if they don’t hurry and use the suctioning straw to remove the liquid, you’re going to swallow!
Do you swallow in your sleep?
A study was done to find that the only times you swallow while sleeping is during arousal and during REM. My logical deduction regarding why is that when you’re aroused or in one of the more shallow phases of sleep, that is when you can voluntarily move – roll over, adjust the bedding, and swallow. During REM sleep, most people will experience sleep paralysis, so whatever exciting things are happening in their brain, the body is not likely to act it out. Because the brain cannot tell if a dream is real or imaginary, the feeling solicited can trigger hormones secretions and saliva production. Increased saliva, just like in the dentist scenario, can trigger swallowing.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Tonsillectomy – Episode 111
What is a Tonsillectomy?
A Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils. Tonsil – immune system tissue in the back of the throat. -Ectomy = to remove something from the body.
Removing the tonsils may be required if chronic tonsilitis is a problem. Chronic tonsilitis is defined as multiple infections in a row or an infection lasting 3 months or longer. Severe snoring and sleep apnea may be another reason to remove the tonsils, for the purpose of opening up the airway.
Adenoids
Adenoids are another set of immune system glands in the back of the nasal cavity. They can also swell during infections and interfere with breathing. Depending on the severity of the infections or the risk of sleep apnea, these may also be removed in the same or a similar procedure.
Tonsillectomy Methods
Since general anesthesia is used in all methods to remove the tonsils, no eating is allowed before the procedure. They also recommend no NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are to be used before and after due to their ability to thin the blood and increase the risk of bleeding. In general, a tonsillectomy will take between 30 and 60 minutes. Recovery time afterward is estimated to be about two weeks.
- Scalpel
This is the old school method of using a very sharp surgical knife to cut out the tonsil. This method has the highest risk of bleeding. - Cauterization
This method involves a hot knife that separates the tonsil tissue from the throat. The heat also closes off the blood vessels so bleeding is not as severe. A downside is that the tissue has been burned, so I imagine the pain after this method is more severe. - Ultrasonic Vibration
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves that have a higher frequency than the human ear hears. The waves cause a very rapid vibration and the energy of those waves is what causes the tissue to separate as well as the blood vessels to clot. This is the newest method developed and seems to have the least bleeding and pain.
After the Tonsillectomy
The side effects of a tonsillectomy include swelling of the throat, as well as the face and jaw, bleeding, and infection. To avoid the bleeding and infection, it is important to follow all the instructions given for the recovery period. Because of the swelling, cold foods like ice cream and popsicles are popular because cold things reduce swelling. Popsicles can also help with hydration because swallowing bigger sips or gulps of water can be painful the first few days. Hot foods are not recommended because the heat can increase the pain or reinjure the surgical site. And while ice cream is the most popular post-tonsillectomy food, any soft, non-abrasive foods are fine to eat.
Why do adults have more issues than kids?
Kids heal faster because they are still growing and developing. Kids also have smaller body parts than adults – the tonsils are smaller and the blood vessels are smaller. Smaller blood vessels clot and heal faster than larger ones. This is even true between the different sized blood vessels in your own body. And a factor no one wants to admit: adults are terrible at following directions and truly resting after a surgery or procedure. Rest is the best thing for a healing body of any age or size.
Strep Carriers
Generally, when we think of severe tonsilitis that leads to a tonsillectomy, we think of strep throat. A carrier is someone who carries the germ around with them but does not get sick from the germ (pertussis is another example). In 1998, a study found that 5-15% of school-aged children were asymptomatic carriers of strep. This means they tested positive on a strep swab but had no symptoms of being sick. This causes concern because it means that you can be sick with something else that causes vague symptoms like fever and sore throat but because the strep test is positive, antibiotics are prescribed when they might not be necessary (meaning that you were sick from a virus). This study showed that providers and caregivers were unaware of the number of unnecessary antibiotics they were prescribing.
Strep is eradicated from a carrier by an extensive treatment of antibiotics, or by removing the tonsils from the carrying family member as well as the tonsils of the chronically sick family member. #tonsillectomyforeveryone
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851340/
Callback
Facebook Memory: Episode 74
Sleep Hygiene
All About Sleep
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Tonsils – Episode 110
Tonsils Basics
Your tonsils can be found in the back of your throat. You can open your mouth and look in the mirror and see them on each side of your mouth behind your teeth and tongue. You can also feel them below your earlobes and behind your jaw bone.
Tonsils are composed of lymph tissue since they are a part of your lymph system. They store white blood cells that help you fight off infection. Their activation during sickness is why they swell and get sore.
They are covered with the same mucosal membrane as the rest of the inside of your mouth. This mucosa layer has pits and crevices called crypts. These crypts increase the surface area of the mucosa that comes in contact with the lymph tissue and allows more opportunity for infectious material to be directly accessed by the immune system.
Infectious Tonsil Issues
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils. It can be classified as acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis is directly related to a viral or bacterial infection. Chronic tonsillitis can be either a persistent, long-lasting infection or multiple consecutive acute episodes that can appear to be one long sickness.
Swollen tonsils can cause simple activities such as swallowing, talking, and breathing very painful. You can see your swollen tonsils when you look in the mirror. They will appear red or possibly blistered.
Mono, an infection caused in adolescents and adults by the Epstein-Barr virus, cause severe swelling in all the lymph nodes, including the tonsils. This is one of the situations where your tonsils will be so inflamed, you can see the swelling on the outside of your face and neck. Because such a large portion of your lymph system is involved, including your spleen, this is a serious sickness.
Strep throat is probably the first infection you think about when you think of swollen tonsils. The bacteria, streptococcus, infect the lining of the tonsils and throat. This is why the doctor will swab your tonsils when they’re testing for strep.
Non-Infectious Tonsil Issues
A non-infectious reason the tonsils will be large is a condition caused hypertrophic tonsils. The tonsil tissue and/or mucosa overgrow and become oversized without any infection or immune activation being involved. Overgrown tonsil tissue can lead to snoring or sleep apnea, and that’s bad.
Another non-infectious issue with your tonsils is called tonsilloliths or tonsil stones. These stones happen when dead bacteria or food debris gets stuck in the crypts and they become calcified. They cause a sensation many describe as a crumb stuck in your throat. They can become quite large and can interfere with swallowing and eustachian tube function. Because the eustachian tubes run from your eardrum into your throat, if the tonsil is swollen enough, it may close off the tube to the ear and cause ear pressure/pain. Some tonsil stones are large enough to be visible and may have to be manually removed. Lastly, due to the composition of the stones (dead bacteria and old food), frequent tonsil stones can be the cause of bad breath.
There’s no way to prevent tonsil stones 100%. Good oral hygiene can certainly help reduce the frequency of stones, and can also help remove them quickly if they occur. The most common way of trying to remove a tonsil stone involve coughing, clearing your throat, or hissing. All three of these ways produce vibrations in the lining of the throat and mouth. So along with the exhalation of these methods, hopefully, the result is the stone coming out of the tonsil and out of your mouth.
PSA: Please DO NOT scratch your tonsils with your fingernails to remove a tonsil stone!
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Metallic Taste – Episode 109

Glossary
Aguesia: no taste
Hypoguesia: reduced ability to taste (no the same as when taste changes due to changes in ability to smell)
Dysgeusia: dysfunctional taste (bad, salty, rotten, or metallic taste). Metallic is most common.
Causes for Change
Chemotherapy and radiation for cancer causes taste changes because the taste buds are rapid-cycling cells and the goal of chemo and radiation is to kill fast-growing cells (cancer cells are definitely fast-growing).
Head trauma or brain damage may damage the path of taste from the mouth to the brain.
Conditions like GERD, diabetes, urinary retention, and dry mouth can cause dysgeusia. Zinc deficiencies can too (in case you can’t tell, zinc plays a big role in many processes in your mouth).
Over 250 medications can causes changes in taste. These include blood pressure medications, antibiotics, chemotherapy, asthma medications, and lithium. Some of them are secreted in the saliva, so the change in taste is because you actually taste the medicine. Other changes are because the medication disrupts or alters receptor or signal transport (i.e. ion transport – sodium, calcium, potassium, or chloride).
My Own Metallic Taste
I was taking generic Biaxin, AKA clarithromycin, for a sinus infection. Clarithromycin is in a class of medication called macrolides. Macrolides work on infections by disrupting the DNA-copying proteins in the bacteria. They are known as bacteriostatic antibiotics, which means they stop the bacteria from growing and dividing, but do not kill them. This allows your own immune system to get rid of the bacteria itself.
It was the worst! Everything tasted so bad. I had to take it for 10 days, so I spent those 10 days eating the strongest and spiciest foods I could find to try and cover it up.
Your saliva contains clarithromycin in a concentration of ~2.72 mg/L. To get an idea of how small this amount is, it takes you 12-24 hours to produce 1 liter of saliva. Only 3-7% of adults report metallic taste with clarithromycin.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Taste Buds – Episode 108

Review
Smell plays a big part in your ability to taste. The bumps on your tongue that you can see are actually papillae.
4 Types of Papillae
Filiform
Filiform papillae are the most numerous papillae and are arranged in regular rows running parallel to the median sulcus. They are cone-shaped – either a single cone (like a volcano shape) or a frill of cones. These papillae don’t actually taste flavors but they do sense touch. They work as cleaners, helping your tongue create friction with other parts of your mouth to loosen bits of food from the nooks and crannies.
Foliate
These papillae are located on the sides of the tongue near the back. They are flat, leaf-like folds, and can be visible in some people. These papillae contain taste buds for flavors.
Fungiform
These are mushroom-shaped. They are scattered all over the tongue but seem to be more concentrated on the edges and tip of the tongue. They contain taste buds for flavor as well as the sense of touch.
Vallate (Circumvallate)
These papillae are dome-shaped with a border. The best description is that they appear as a circular fort with a mote around it and then a wall on the outside. Or maybe they look like a bunch of “outie” belly buttons! They are laid out on the back of the in a V-shaped pattern, pointing towards the back of the throat. These papillae can be visible in some people, and they contain taste buds for flavors as well.
Each papilla contains many taste buds. They are called “buds” because, microscopically, they appear as unopened rosebuds. Taste buds have a swirl-like funnel with an opening in the middle that contains fluid.
How You Taste
You put food in your mouth. Your saliva dissolves bits of it to free up molecules. The molecules that are mixed in your saliva wash into the funnels of each taste bud. There, the molecules mix into the taste bud fluid and get swirled around to come in contact with as many taste sensors (nerves) as possible. From here, the chemical signal changes into an electrical signal as the taste messages zoom into your brain. In the brain, the signal is translated and identified – including details such as flavor, pain, temperature, texture, intensity, and smell (while your saliva mixes with some molecules, other molecules are released into the air as aromatics and contact the olfactory sensors in your nose).
Taste Buds Map Truth
The taste bud map that has been used for years in textbooks was created in 1901. Even with all the things that we’ve learned about how taste buds work, where they’re located, and what they look like, this map has never been re-written. The original map identified four basic flavor categories: sweet, sour, salt, bitter. Yet, just nine years later, the Japanese were able to identify “umami” – that savory flavor that doesn’t quite fit into the other four. Yet, the map still wasn’t re-written. Even now, scientists are learning and updating the database on what the tongue can taste and how – including categories like “fatty” and “metal” and even “water”.
So, while the taste buds are not grouped into sections based on the flavor they can taste, some taste buds may have a greater affinity or sensitivity to a certain type of flavor.
It is estimated that we have about 2000-4000 tastebuds, and since the surface of the tongue is like your skin, the tastebuds recycle about every week or two. This rapid and continuous recycling might be why it is acclaimed that your taste (preference and enjoyment from your taste buds) changes approximately every seven years.
Conclusion
Even though the tastebud categories are still too complicated to rewrite the map, I still plan to use my taste buds to their fullest potential. Eat up!
Resources
I gathered some of my information from a PubMed article that is actively being updated by real scientists – How Does Our Sense of Taste Work?
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Burning Mouth & Pepto Lips – Episode 107

Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning Mouth Syndrome is defined as a burning sensation with no underlying cause. It may include dry mouth sensations with no true symptoms of dry mouth. BMS is accompanied by unremitting burning or pain but no mucosal changes or signs of injury or swelling.
3 Categories
- Increases throughout the day after waking
- Stays the same morning, during the day, and at night
- Has no pattern
Common Symptoms
- Bilateral pain of the tongue
- Chronic pain labeled as moderate to severe, or a 6-10 on the pain scale.
- Worsened by talking, stress, fatigue, or hot, spicy, or acidic foods.
Subjective Descriptions
- Dry mouth
- Change in ability to taste
- Accompanied by a headache
- Decreased appetite
- Improved by cold foods or drinks
Those who suffer from BMS may see temporary relief with topical analgesics (i.e. lidocaine or benzocaine) but see no improvement from systemic medications. Fifty percent of the cases have no apparent cause but do have some correlation with depression. This is a case of “the chicken or the egg”. Are people with depression more likely to have symptoms of BMS? Or are people with BMS more likely to become depressed?
Before someone can be said to have Burning Mouth Syndrome, many other issues must be ruled out.
- Deficiencies (iron, folate, B vitamins, zinc)
- Dry mouth
- Nerve damage
- Hypothyroidism
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Nocturnal habits (clenching, grinding, tongue-thrusting)
- Infection (thrush, herpes, HIV)
- A hiatal hernia (GERD)
- Medications (ACE inhibitors, anticholinergics)
- Myeloma (a blood cancer involving plasma cells)
Pepto Lips
Pepto-Bismol, aka Bismuth subsalicylate, has been used for decades for a variety of stomach complaints.
Bismuth is a good binder of toxins, in a similar way that carbon is in activated charcoal. And yes, bismuth is one of those elements on the periodic table. Subsacylate activates into salicylic acid (related to aspirin) and works to decrease inflammation of the gastric lining.
When bismuth binds with sulfur that is naturally in your saliva, it becomes bismuth sulfide, which has a black color and can stain your tongues and lips temporarily. Pepto overuse is the obvious cause of black lips.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Tongue Issues – Episode 106

Born With…
Ankyloglossia is also known as a tongue tie. It is a result of a short frenulum. This issue is easily corrected if it interferes with eating and talking.
Macroglossia is am abnormally large tongue. This is one of the visible characteristics of Down’s Syndrome. It is described as the tongue looks and feels to be bigger than space in the mouth.
Infected With…
Strawberry tongue
The tongue can appear extremely red and papillae are swollen to look like seeds on a strawberry. This is a symptom of several conditions.
- Kawasaki Disease is a rare but serious childhood disease. The blood vessels become inflamed, and this includes the blood vessels in the tongue, making it appear red.
- Scarlet Fever is caused by the same bacteria as strep throat. The infection goes from being just in the throat to the bacteria toxins spreading in the bloodstream.
- Toxic Shock Syndrome is when the bacteria called Staph aureus (yes, this is the staph that lives on your skin and can cause wound infections) gets into the bloodstream. This is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Hairy Tongue
White hairy tongue appears as patches on the sides of the tongue. It can happen when someone who is immunocompromised gets the Epstein-Barr Virus. (Epstein-Barr is a virus that causes mild childhood illness or a disease we know as Mono when teens and adults.)
Black hairy tongue is a little more obscure with several possible root causes.
- Smoking, excessive coffee or tea consumption, excessive alcohol consumption, or soft diet can lead to the inability to shed dead skin cells.
- Antibiotic overuse leads to overgrowth of fungus or bacteria.
- Overuse of peroxide-based mouthwash causes oxidation and discoloration of the skin cells.
Function Lost
Motor Neuron Disease occurs in the later stages of ALS or Lou Gerig’s Disease when the nerves and muscles of the tongue for speech and swallowing become affected.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Your Tongue – Episode 105

Tongue Basics
Your tongue is made up of eight muscles. This is why it is called a muscular organ. It is the most important articulator in speech production. (A brief word dissection: articulate means to communicate something clearly. In medicine, articulate means to make a connection. It all makes sense!)
The tip is called the apex. The crease down the middle is called the median lingual sulcus. There is another crease at the back of your tongue and it is called the sulcus terminalis.
Tongue Muscles
The tongue has two types of muscles. Extrinsic muscles attach to bones boarding the mouth. Intrinsic muscles are completely contained inside the tongue borders.
Extrinsic Muscles
These muscles are responsible for moving your tongue front to back and side to side. There are four of them and they are named for the facial bones that they are anchored to.
- The genioglossus muscle moves it forward so you can stick it out of your mouth.
- The Hyoglossus muscle pulls it back and presses it down.
- The Styloglossus muscle raises the sides of it during swallowing.
- The Palatoglossus muscle raises the back of it during swallowing. It also presses the soft palate down and squeezes the palatoglossal arch inward during that same step of swallowing.
Intrinsic Muscles
These muscles are responsible for all the shapes and movements your tongue makes when you talk and eat.
- The superior longitudinal muscle covers the top side.
- The inferior longitudinal muscle covers the bottom side.
- The vertical muscle fibers are in the middle and connect the superior to the inferior muscles.
- The transverse muscle fibers start at the median sulcus and connect to the outer edges.
The Tongue Has Skin?!
The surface of your tongue is known as the masticatory mucosa, which basically means it’s the surface that food comes in contact with. The surface is made up of epithelial cells just like your skin. The cells are keratinized (or filled with a toughening protein) so it is tough and does not get damaged by the wide variety of things we eat.
Call Backs
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Teeth Issues – Episode 104
Teething
Teething is mostly known as the phase of babies growing their first teeth. Eruption is when the tooth enamel shows through the gum tissue. A baby’s first teeth grow in between 6 months and 2 years old. Before any of the teeth show, the gums can be swollen and bumpy. These symptoms can cause fussiness, sleeplessness, drooling, decreased appetite, excessive chewing, and overall grumpiness. A few controversial symptoms include fever, diarrhea, and rash. A fever less than 100.4*F can be indicative of inflammation going on, which can be true for some teething babies. Diarrhea is blamed on excessive saliva ending up in the digestive tract (eh, many things can change the consistency of a baby’s poop, especially in the early stages where they’re only drinking milk or just learning to eat new foods). A rash is a little more questionable, but can also be a result of inflammation going on.
Treatments
Treatments for teething babies include Infant’s Tylenol or Infant’s Ibuprofen (for children older than 6 months). Other medications that used to be recommended for teething babies were Teething Tablets and Orajel. An active ingredient in the Teething Tablets is Belladonna. This medication can constrict blood vessels, which is good when there’s inflammation (increased blood flow) to an area, but bad when baby’s blood vessels are already tiny and they need to get blood to very important places (i.e. the brain). The bottom line is that Belladonna can decrease the amount of blood, and therefore oxygen to a baby’s brain, and the outcome can potentially be SIDS.
This is also true of Benzocaine, the ingredient in Orajel. Benzocaine is a topical numbing agent. The key word here is topical. It is not intended to circulate in the body. The problem comes when you use a TOPICAL product in your mouth, you can’t help but swallow some of it. When Benzocaine is swallowed, it can cause a serious side effect that involved decreased oxygen in the blood. Again, if oxygen doesn’t get to important places in the baby’s body, bad things can happen.
PSA: NO Belladonna and NO Benzocaine for babies!
Plaque
Your teeth are covered in a biofilm that is mostly made up of bacteria. That bacteria can compromise the seal that is formed between healthy teeth and healthy gums. If this seal is breached by bacteria, then infection and gum disease (gingivitis) can occur.
Tartar
Plaque can harden, and when it does, it becomes known as tartar. Mouth bacteria eat the sugars in the food that gets stuck in the crevices of your teeth. A waste product of this process is lactic acid, and lactic acid can actually dissolve enamel of your teeth. Minor erosion can be repaired by your body. The problem is that saliva cannot break through the plaque.
Cavities
Tooth decay is the result of long-term enamel erosion that can’t be repaired by the body. If the erosion is deep enough, it can expose the softer parts of the tooth to irritants and injury. When this happens, the only way to repair and protect the tooth is to get a filling from your dentist. *womp womp*
Discoloration
Extrinsic stains are when substances change the tooth color from the outside. So this is how coffee, tea, wine, and tobacco can make the teeth yellow or brown. Also, certain bacteria, excessive chlorophyll, or excess copper and nickel can make the teeth look green.
Intrinsic stains are when the building blocks of teeth are altered and changes the color from the inside. Tetracycline antibiotics have been a common treatment for acne in teenagers for quite a long time. It is well-documented that these antibiotics can bind up free calcium in the body. Therefore, it is not recommended for pregnant women or children younger than 8 years old to use these medications. There are many cases of developing fetuses and children with quickly-developing teeth ending up with grey or brown teeth due to this missing calcium (remember, calcium built into the enamel is what makes it white).
Injuries
A chipped tooth is when a part of the enamel breaks away. A fractured tooth is when a crack involves the enamel and the dentin. An abscess is an infection in the gum around the tooth or in the accessible or exposed pulp of a tooth. Luxation is a dislocated tooth, and may or may not include injury to the periodontal ligaments or jawbones.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Teeth – Episode 103
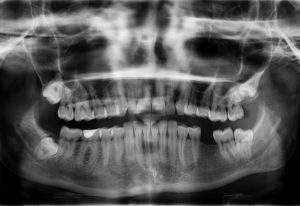
Types of Teeth
Incisors: You have 4 on the top and 4 on the bottom. Yes, it sounds like “scissors”; they are the teeth and cut and tear food (or the enemy?). They are in the very front of your mouth.
Canines: You have 2 on the top and 2 on the bottom. Yes, canine, like a dog; they are sharp and pointed. These teeth are good for gripping and tearing. Also known as cuspids (one point). They are located at the “corners” of your teeth arch.
Premolars: You have 4 on the top and 4 on the bottom. These are permanent teeth only. They have a flatter surface for crushing food. Also known as bicuspids (two points).
Molars: You have 6 on the top and 6 on the bottom. They have large flattish surfaces for grinding up food. Four of these molars are also known as your wisdom teeth.
Parts of a Tooth
Outside In
Enamel: This is the part that you can see. It is mostly made up of a crystalline structure of calcium phosphate, and that’s what makes them look white. Enamel all by itself can be very brittle.
Dentin: This layer is made of a softer, yet still strong calcium-containing crystals. This acts as a tough and supportive scaffold for enamel.
*These two layers together are what make your teeth so hard and strong.
Pulp: The soft connective tissue that contains the nerves and blood vessels that feed the tooth.
Top to Bottom
Crown: This is the part of the tooth that is above the gum line that you can see. And since you can only see the outside of the tooth, when you look at your teeth, you only see enamel.
Neck: This is the enameled part of the tooth that is below the gum line.
Root: The part of the tooth that is embedded in the jawbone and provides the openings for the nerves and blood vessels to run up into the pulp. The roots are covered by a specialized bone structure called cementum (yes, it sounds like cement).
*The roots are actually attached to the jawbone by periodontal ligaments. (Ligaments are connective tissue that connects bone to bone).
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Mouth Issues – Episode 102

Mouth Issues
Ulcers
They are uncomfortable and mostly non-serious. Also known as “canker sores”. Can take 2-3 weeks to completely heal. Anything lasting over 3 weeks should be checked out by your doctor or dentist. Ulcers can appear on the inside of the cheeks or lips, the roof of the mouth, or the tongue. A minor ulcer versus a major ulcer is determined by the size of the sore and the layers of skin affected. Any ulcer that is bleeding should be checked out despite the length of time. The edges are red while the center can be yellow, white, or grey. And they are PAINFUL!!
Ulcers can be caused by acidic or spicy foods, braces, stress, hormones, and some medications (such as beta-blockers for blood pressure or NSAIDs). Nutritional deficiencies can increase your risk of ulcers. Malabsorption due to conditions like celiac or deficiencies in B-vitamins and iron are the most common culprits. Also, decreased immunity can make the skin inside the mouth more prone to ulcer recurrence.
Thrush
This is a yeast infection the mouth caused by the overgrowth of Candida, known as oral candidiasis. It appears as white patches on the inside of the cheeks, tongue, or roof of the mouth, and the spots cannot be scraped off. Candida is normal in the body and is kept in balance by the rest of the body’s normal flora. Overgrowth can occur after antibiotic treatments, during times of decreased immunity due to treatments or disease states, or from inhaled steroid treatments.
Thrush is treated with a topical antifungal that the doctor directs you to swish around in the mouth to coat the affected areas, usually Nystatin. If yeast is wide-spread, a systemic antifungal will be used. Probiotics are a great way to keep your normal flora in balance.
Angular cheilitis (ky-ly-tis)
Cheilitis = inflammation of the lips. This is the cracking that can occur in the corners of your mouth. Many sources will tell you this is caused by a vitamin deficiency – like B-vitamins, iron, and zinc. Other times, it may be a wound caused by contact dermatitis from increases contact with the tongue or your hands, and then they may become infected with normal skin bacteria or other bacteria in saliva. An infected wound is one that doesn’t ever appear to heal. Fungal infections, in the same way, cause the skin to crack open and appear overly dry and never-healing.
Lie Bumps
Transient Lingual Papillitis (swollen taste buds). They can appear to be white or red, and they can be asymptomatic or very bothersome. Not sure what exactly causes it. Definitely NOT caused by lying. *I used to think they were “lye bumps” as in sodium hydroxide that is a strong base and used to be popular as a detergent.*
Cleft lip/palate
A birth defect that has a strong genetic component, but also linked to environmental components that have not been pinpointed yet. A cleft lip or palate is a result of parts of the mouth and face not fusing together during fetal development, and requires surgical correction after the baby is born. The oral and nasal cavities are supposed to be separate and when they are not, it can increase the risk of sinus and ear infections. Ear tubes are usually recommended.
Even after repair, a child may require speech and occupational therapies to develop the muscles needed for normal speech and eating habits. Many times, a follow-up surgery is required as the child grows, and many other types of mental support are needed.
Bonus
*Mouth Cancers: the most common cause of mouth cancers is tobacco use (smoking, chewing). It can start out as something that appears minor like a mouth sore, but can develop quickly into something deadly. In the end, it can result in large areas of the mouth having to be surgically removed.
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Mouth Parts – Episode 101

Mouth Parts
Lips: They are red due to blood flow. They have lots of nerve ending so they can be very sensitive. Our lips are used to manipulate food as we eat and make sounds as part of our speech.
* The Divot above the center of your upper lip is called the philtrum.
Gums: They are also known as the gingiva. Even though they are wet and look fleshy, healthy gums are quite resilient.
Teeth: They are used for chewing, and possibly as a tool. Healthy teeth and gums seal together tightly to keep out invaders. We will talk about teeth in a separate episode.
Tongue: It is a muscular organ made up of many muscles and nerve endings. It just happens to be an organ that we can voluntarily move around. We use our tongue to manipulate food and to make sounds for speech. And, of course, it is covered in taste buds. We will cover all of this in a separate episode.
Hard Palate: A flesh-covered bone that connects the upper teeth. Our tongue will smash food against it when we eat and use to make certain sounds in speech.
Soft Palate: It is a muscle behind the hard palate and it moves up to close off the nose when we swallow and sneeze. It also interacts with the back of the tongue to make certain sounds when we talk.
Palatoglossal arch: It marks the front edge of the soft palate.
Palatopharyngeal arch: It makes the back edge of the soft palate and the end of the “mouth”.
Salivary Glands
Parotid glands: The largest salivary glands are located by your jaws, below your ears.
Submandibular glands: They are located under the jaw and back molars
Sublingual glands: They are located under the tongue, behind your chin.
~1000 of mini glands: They cover the buccal (cheek) tissue, soft palate, uvula, and tongue to keep everything moist. This is what allows the inside of the mouth to be known as a mucous membrane.
Sublingual papilla: This is the folds of skin under the tongue. This area contains many blood vessels close to the surface. Medicine development has learned this is a great place for medication absorption directly into the bloodstream.
Palatine raphe (ray-fee): This is the seam down the middle of the hard palate.
Frenula: Plural for frenulum. These are folds of skin that connect one place to the other. You have three: for your upper lip, lower lip, and tongue.
Uvula: Latin for “small bunch of grapes”. It is attached to the soft palate and contains a gag reflex trigger. It is also involved in snoring if it dries out.
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI
Manifesto

Post-Manifesto Tidbits
This is the heart and soul of why I have produced this podcast for 100 episodes. My Manifesto, if you will.
The podcast is going to take a break for the summer to regroup and plan new and fun things!
In the meantime, catch up on episodes you missed or re-listen to them all!
If you want to stick close for sneak peaks of new adventures and the reboot, join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
If you’ve enjoyed the first chapter of The Pharmacist Answers Podcast, please leave a rating and review on your favorite podcast app.
The new home for show notes is intelleximed.com
Thank you so much for letting me be in your ears each week.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Sneezing [Show Notes]

Sneezing is very forceful in your body.
Review
The inside of your nose is covered with mucous membranes, and that mucus traps up things so they don’t get into your lungs.
Some little particles float through the air and into your nose. They will land on those mucous membranes and irritate it. That irritation sends a signal to your sneeze center of your brainstem.
Callback
Sneezing Details
The sneeze center sends out several signals. One goes to your diaphragm to tell it to compress the lungs to force the air out. Another signal goes to your tongue to have it direct the air through your nose. The last signal goes to your eyes – it is really true, you can’t sneeze with your eyes open.
So your abs contract and your diaphragm forces your lungs to exhale, your tongue directs the air to go out your nose, so the mucus plus the things that irritated your nose flies out of your face.
*Mythbusters sneeze experiment*
The proven statistics on sneezes is that they travel about 40 mph but only go about 20 feet.
Holding in a sneeze can be painful and damaging. By holding in all that air, you can rupture your eardrums, damage your tear ducts in your eyes, fracture your nasal cartilage or bones, or cause nose bleeds because of the blast against your sinus passages.
Sneezing Advice
There’s so many tricks about trying to stop a sneeze – most of them involve counter-pressure on other spots on your face or body.
The best advice for stopping a sneeze is to blow your nose to get out the irritants before the body blasts it out with a sneeze.
You will never ever sneeze when you’re sleeping. So morning sneezing fits are normal for a lot of people. This is because all the dust and stuff you breathe in while you’re sleeping finally irritates your body. So morning congestion and sneezing is normal to help clear all of that out.
We’re unsure why people will sneeze in other situations like sudden exposure to bright light or changes in air pressure or temperature. Another unsual trigger is an over-full stomach. Multiple people have reported they feel nauseous and once they sneeze, the sick feeling goes away. I dunno….
If you do have to sneeze, make sure you cover your face. Use the elbow technique!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Nose Issues [Show Notes]

Nose issues that cause your breathing to fail
- Congestion from allergies, viruses, or infections.
- Deviated septum – the septum (the bone that separates the nasal cavity and divides your nostrils) can get crooked and change the size and access of the nostrils or nasal cavity. Can be from trauma, or may gradually get crooked from chronic pressure.
- Turbinate Hypertrophy – over-growth of tissue covering the turbinates (tissue-covered bones that add warmth and moisture to the air you breathe). This can lead to snoring. May be treated by steroid nasal sprays or surgery to remove extra tissue.
- Nasal Polyps – uneven overgrowth of mucus membranes (symptoms may be runny nose, post-nasal drip, stuffiness). They are not cancerous. Treated by snipping them out.
- Sinus cancer – a single growing tumor that causes bulging, either around the eye, face, or mouth.
Nose issues that cause your smelling to fail
- Age
- Deviated septum (see above)
- Polyps (see above)
- Chronic sinus infections – the smelling sensors are inflamed or covered with mucus so much that they become damaged or less sensitive.
- Smoking – smoke and toxins can damage smelling receptors in your nose. Also, the receptors become so clogged up with smoke and tobacco molecules that there’s no room for other molecules to be detected. This can be temporary or permanent.
Nosebleeds
- In kids, this is usually from trauma (either bumps and bonks or picking). Can also be caused by dry air in the wintertime (use vaseline in the nostrils).
- In adults, can be from hypertension (high blood pressure) or chronic use of blood thinners.
PSA: Treatment for a nosebleed: DO NOT tip your head backwards!!!!! It makes you swallow that blood! THAT’S GROSS!! Proper treatment: pinch the nose and tip the head forward. This allows a clot to form and clots stop the bleeding.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Smell [Show Notes]

Smell Basics
Air goes in your nose and flows over the smell sensors.
Your nose and sinus cavities act as a resonating chamber for your voice. That’s why you sound funny when you hold your nose or when your nose is stopped up from a cold or allergies. This is important in talking and singing.
What makes something smell?
Volatile molecules evaporate at normal temperatures and pressures, so actually molecules of the thing are in the air and available to go in your nose. Don’t think about this too hard….
The smelling sensors are on the roof of the nasal cavity –> olfactory receptors (olfactory is the fancy word for smelling). The molecules fit into the receptors like a key in a key hole. Our brain likes to categorize things, and so certain compounds have similar structures and get lumped together (“smells like eggs” but you know it’s not real eggs).
The olfactory receptors send the signals to the olfactory bulb (which is the area in the brain that translates all the smells and allows you to identify a smell). It’s not a very long trip….
The olfactory bulb is a part of the limbic system (the emotion center). this is why smell is more strongly connected to emotions and memory – even stronger than sight and sound.
Smell Tidbits
If you go to the perfume counter at a department stores, you’ll find that they all start smelling the same. The perfume department will have coffee beans because it helps clean out the receptors.
Coffee-scented, caffeinated perfume <– free idea!!
Inflammation and mucus congestion blocked off the receptors.
No concrete evidence of why pregnant women get a “super smeller” during pregnancy.
One rogue molecule won’t make you smell something.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Nose Anatomy [Show Notes]

Nose Basics
Your nose is responsible for breathing and smelling. These things work better when it isn’t stopped up.
The part of your nose that you can see and touch is cartilage covered in skin. There is bone above it, beside your nose, below it, and right in the middle (inside your head). Part of the cartilage is stiff and hold shape, other parts of cartilage are soft for flexibility.
The nasal root (the bone that extends between your eyes) connected to the bridge of your nose (which is made of cartilage). The tip is also called the lobe. The wings are on each side of your nose that you can flare. The nostrils is actually the holes.
There are 4 main sinus cavities
- Frontal sinuses = in your forehead, between your eyebrows
- Maxillary sinuses = run under your eyes, behind your cheeks
- Ethmoid sinus = right between your eyes, in the middle of your head, connected to your tear ducts
- Sphenoid sinus = under your sphenoid bone (in the middle of your head)
The sinus cavities are lined with mucous membranes that keep them moist and have lots of blood flow to them. Their job is to warm and moisten the air you breathe in your nose before it goes into the lungs. Your lungs don’t like cold air.
Mouth breathing is not very efficient. This is true in athletics as well as sleep. But breathing out through your mouth can be useful because you can get a large amount of air out rather quickly and the lungs empty better.
You have a fast-flow and a slow-flow nostril – this has to help you perceive smell. Sometimes almost as good as dogs.
The cartilage of your ears and nose never stop growing through your life.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Ear Issues [Show Notes]

PSA: Please don’t stick things in your ear any larger than your elbow…and that includes your finger.
Review
Outer ear = the part that you can touch
Middle ear = the area being the ear drum
Inner ear = the cochlea and area responsible for your balance
3 common ear problems
- Ear infections (otitis media)
- Vertigo (and motion sickness)
- Tinnitus (ringing in your ear)
Callback
Ear Infections
The area behind your ear drum has air in it and that pressure is equalized through the eustachian tube. If that area gets fluid in it, that fluid can grow bacteria and that leads to infection. The natural motion of opening and closing your jaw helps massage the eustachian tubes and moves air in and out (like when you fly or drive in the mountains and you chew gum or yawn).
Cold and allergies can be the source of the fluid build up that leads to ear infection. You may have decreased hearing, pain, decreased balance – infection can require antibiotics.
Vertigo
This is the sensation of spinning, dizziness, being off balance
The semi-circular canals are responsible for your balance. If it get sloshed too much, or doesn’t level out exactly right, then the signals sent to the brain may translate to being off balance even though your body is upright. The signal confusion is what can lead to nausea (it’s not actually happening in your stomach – at least not until you vomit!)
The fluid moving around in these canals are why kids can induce dizziness when they spin around in circles (think about the clothes in your washer during the spin cycle – they get pushed to the outside).
Medications for vertigo are the same as some medications for nausea – plus they have drowsy side effects, so maybe you just sleep it off.
There are many suspected causes, but nothing definite or proven.
Tinnitus
Defined as ringing, buzzing, roaring, whooshing sound when nothing is actually making that noise.
Causes: hearing loss (either due to aging or exposure to loud noises); high blood pressure (pulsating); medications
One theory: the hairs in the cochlea are damaged so those frequencies of sound (usually high pitched sounds) can’t be picked up anymore; the brain fills in the gaps with “made up sound”. This is NOT PROVEN!
High blood pressure can cause you to hear the blood pulsing through the blood vessels in your ears.
Medications that causing ringing in the ears
- Aspirin (acute over-use)
- Aminoglycosides (i.e. Gentamicin = antibiotic) – it has a small therapeutic window, too much can lead to ear damage, it stopped in time, permanent ear damage can be avoided
- Quinine = usually asked for to help leg cramps, also medically prescribed to prevent malaria. Can only be readily consumed by drinking tonic water.
Flavonoids are put in vitamins and advertised to help tinnitus. Flavonoids are phytonutrients (nutrients you get from plants). These nutrients can’t grow the hairs back in the cochlea. Most of the vitamins and nutrients in the flavonoid vitamins have anti-oxidative properties, but I doubt that tinnitus is a major oxidation problem.
Audience Question
Can being slapped over time cause ringing in the ears?
- Being bopped in the face and head can probably cause permanent damage to the structures on the inside and outside of your head. Being hit in the side of the head can cause pressure build-up in the ear where the air causes the ear drum to rupture (like “boxing” the ears).
- Slaps to the face (like “you jerk!” kind of slaps) don’t usually cause ear problems, but punches or slaps to the side of the head near or on the ears can possibly cause damage.
Prevent ear problems: be nice to your ears!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Ear Anatomy [Show Notes]

Ear Basics
The auricle is the part of the ears you can see. It is made of cartilage (flexible tissue that doesn’t have a large blood supply). Everything else requires a tool for the doctor to see inside. And the doctor can only see to the ear drum. The stuff behind the ear drum isn’t visible because of the membrane that blocks it. The middle and inner ear are surrounded by your head bones.
Science of Sound
Sound is created when the air around us is compressed and then expands. They move away from the source in circles (think radar or sonar or throwing a pebble in a pond).
The ear canal directs the sound waves towards the ear drum.
Sound gets translated in 2 main ways
- Identify the sound
- Identify if the sound has meaning
Inside Your Ears
The ear drum (tympanic membrane) vibrates according to the intensity of the sound and trigger the Hammer-Anvil-Stirrup cascade.
- The ear drum vibrates the handle of the Hammer (Malus bone – yes, it’s a real bone).
- The Hammer bangs on the Anvil (Incus bone).
- The Anvil has a tail that is connected to the Stirrup (Stapes bone).
- The Stirrup looks like the spurs on the back of boots. It is connected to a membrane on the Cochlea and works like a plunger.
All of these bones are surrounded by air and the pressure is controlled by the Eustachian tube. This is the access point for ear infections or congestion due to allergies or a cold.
The Cochlea is a bone full of fluid and lined with hairs and shaped like a spiraled sea shell. The hairs pick up different frequencies of sound (sound wave frequency determines pitch). If certain levels of hairs get damaged, then you will not be able to hear pitches in that range anymore. If you unrolled the cochlea, it would be laid out low pitch to high pitch like a piano. And these hairs are connected to the auditory nerves and turn sound signals into electrical signal to send it to your brain.
Semicircular canals of the cochlea are little bone chambers full of fluid and they control balance. This works like a leveling bubble to help you stay upright. If it becomes dysfunctional, then it may trigger vertigo.
The middle ear (the area behind the ear drum) is where most of the trouble happens – whether allergies causing stopped up ears, or colds leading to ear infections.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Allergy Testing Experience [Show Notes]

Allergy Basics
Anaphylaxis = an out of control allergic reaction that can be life-threatening if medical treatment is not sought immediately
EpiPens are a first-step self-treatment in the case of a major allergic reaction or anaphylaxis.
My Allergy Testing Experience
I got 33 injections!!
Allergy testing started with a serum test as a baseline – just to see how strongly my histamine reaction was.
The injections are sub-dermal (under the dermis layer of the skin). It’s the same level if injection that a TB skin test is done (to see if you’ve been exposed to tuberculosis).
The next step was a prick-test or scratch test – these plastic claw things that poke down in my forearms. This test required me to sit completely still for 20 minutes. COMPLETE TORTURE!
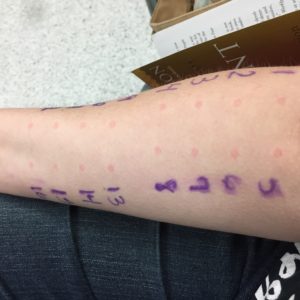


Numbers 1-20 are plants (trees, grasses, flowers). C = cat. D = dog (Good news – I’m not allergic to dogs!) M = skin mites (don’t think about this one too hard). CL = cockroaches. The other letters are household and common molds.
The skin pricks on my forearm was a preliminary test to determine how much serum she was going to inject of each in my upper arms. The mites injection hurt the worse of all of them, but i had minimal reaction.
Slowest tattoo EVAR!
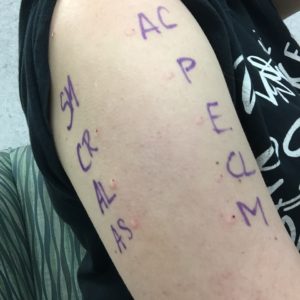

My Results
One of my higher reactions was to Fescue (this is the type of grass that Ken grows on the farm as hay to feed the cows!)
The one the nurse was most concerned about was Cocklebur.
They didn’t want me to wash the mold markings off until I go in for a delayed reading a few days later.
The next step that they prefer you do is allergy shots – 2 years of weekly injections of what you’re allergic to in hopes to desensitize you to those triggers. NOPE! Not doing it!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Conditions 4 [Show Notes]

Eye Conditions (not) in ABC Order
Dry eye
48% of Americans over age 18 complain of dry eyes. Caused by environment, genetics, health conditions, eye procedures, medications.
There are 2 reasons for dry eye:
- Inflammation blocks the free flow of fluid through the eye.
- Tear duct insufficiency – the ducts and glands don’t produce adequate moisture for the eye (can be solved by a tear duct stent)
If a medication dries up another part of your body, then it has the potential to dry out your eyes (antihistamines, medications for overactive bladder) – these medications can also lead to constipation. Many of the common diseases that many Americans deal with can cause dry eye – hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes, obesity.
They light from electronic devices tricks your eyes into not blinking as often, therefore your eyes can dry out more easily (blinking is your eyes’ remoisturizing process). The solution is to give your eyes long breaks from electronic light , especially late at night before sleeping.
Air conditions in hotels can make your eyes feel dry because they work to remove excess humidity from the air.
Hormones, whether in pregnancy, menopause, or during the use of prescription birth control products, can cause changes in the moisture content of your eyes.
The Solution: eye drops (either OTC or Rx)
Presbyopia
It means “old or elderly vision”.
Presby = elders
Presbyterian church = the church’s decision-maker was a group of people called Elders
This seems to happen somewhere around age 40. The lens of your eye loses some of its flexibility. The lens has to be really curved to see up close, and then flattens out a bit to see far away. So, if the flexibility decreases, it means it can’t curve up enough to clearly see things up close.
The solution: wear reading glasses.
Stye
It’s an infected oil duct or hair follicle. Looks like a zit. **DO NOT TRY TO POP A STYE LIKE A ZIT!!** They will usually clear out on their own in 6-7 days. Not too troublesome other than being sore, swollen, and not pleasant to look at.
The Solution: warm compress for 15-20 min, then take a shower or wash your face, then leave it alone! Can use drops or an ointment to help lubricate the eye. Worst cases will require antibiotic drops or ointment from the doctor.
Corneal dystrophy
A genetic condition that causes the accumulation of protein material build up in the layers of the cornea (recap: cornea = the very front layer of your eye that starts to focus the light into the eye). If this fluid gets cloudy with junk, then your vision gets blurry. No other symptoms really except worsening vision. A surgical procedure can be used to clear out the cloudy liquid, but no cure.
This can lead to corneal erosion (where the layers of the cornea begin to separate = painful). Corneal erosion has to be corrected by surgery. Erosion can also be a result of eye injury – either instant trauma or more gradual like an unhealed corneal abrasion (which can lead to ulceration and eventually erosion).
Take care of your eyes and treat them nicely!
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Conditions 3 [Show Notes]

Eye Conditions in (not) ABC Order
If something happens to your eyes that makes you want to ask the pharmacist if you should go to the doctor, the answer will most likely be “yes, go see a doctor.” Even at emergency rooms, they will treat you and make you comfortable but always tell you to follow up with your eye doctor.
Photopsias
This is seeing things that aren’t really there, the visual cortex translates other sensations as “sight”.
- Floaters: “shadows” that float around in your field of vision. They *can* be a sign of a detaching retina, but that is usually not the case. They are normal for most people.
Inside your eyeball is a gel, called vitreous gel. Throughout your life, that gel begins to liquify. As it turns to liquid, it may have other bits of gel still floating in that liquid. And you see “shadows” because they block light from reaching your retina. Floaters may worsen with dehydration or exhaustion. If you try to focus on them, they “float” away. - Flashes: “seeing stars” – when the vitreous gel/liquid combo gets shook up and sloshed around (i.e. head trauma). You can also get “flashes” with Digitalis toxicity (Digoxin is a medication derived from the Foxglove plant and developed for arrhythmias.) This is a medication that the doctor will test your levels for to make sure toxicity doesn’t happen.
- Waves: looks like radiating heat; caused by spasms of the blood vessels in your eyes. This may be one explanation of the “aura” that comes before a migraine. If it happens and no headache follows, it’s caused an “ocular migraine”.
Glaucoma
It is the 2nd leading cause of blindness in the US and around the world. Glaucoma is known for increased pressure in your eyes. The fluid around the eyes typically have adequate drainage so nutrients can flow in and waste can flow out. If that drainage becomes inadequate, the pressure builds up and it can put pressure on the optic nerve (the nerve that connects from the retina to the brain). It starts with decreasing peripheral vision, and can become “tunnel vision” where a person can only see right in the middle of their field of vision. Medications are eye drops that control pressure and help open up drainage pathways as much as possible. It doesn’t hurt, and it takes a while for the decreased peripheral vision to be noticeable. It’s not reversible, but it can be slowed with medication. Eye doctors have a way to check the pressure in your eyes each time you get your eyes checked.
(Macular Degeneration is the #1 cause of blindness in the US, Cataract is the #1 cause of blindness worldwide).
Nystagmus
Pronounced nigh-stag-mus. It is the involuntary rapid eye movement side to side. Caused by a neurological issue, either related to the eye muscles and nerves or the inner ear (one cause a vertigo). The shaking seems to be worse when a person looks straight at something or someone. For someone dealing with nystagmus, they usually discover they can tilt or turn their head to make their eyes slightly off center where the shaking wills stop – this is called a “null point”. Strengthening eye muscles can help the shaking, but it still worsens with exhaustion or stress.
This can be a result of a stroke, multiple sclerosis (autoimmune). Dilantin is a medication for seizures, and is another medication that has to be regularly measured because too much can cause temporary nystagmus.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Conditions 2 [Show Notes]

Eye Conditions in ABC order
Color blindness
It doesn’t mean that someone sees the world in black and white.
It’s technically labeled as Red-Green color blindness, which means the world is seen in shades of yellow.
The cones in your eyes (a certain shaped cells in your retina) are built to pick up different wavelengths of light (think ROYGBV). So the cones that would pick up reds and greens are absent or broken.
Found to be a Y-chromosome trait, so it is more prevalent in males.
Rarely Blue-yellow color blindness is a thing.
Conjunctivitis
pink eye = inflammation of the conjunctiva
conjunctiva = the layer that covers your whole eye
3 types:
- Viral: itching, watering, burning, light sensitivity, very contagious, lasts ~ 7 days
- Bacterial: green/brown discharge (aka “goo”), foreign-body sensation, contagious, can cause damage if untreated, requires antibiotic drop
- Allergic: triggered by allergens, histamine reaction, can accompany a larger, more general allergy reaction, anti-histamine eye drops can help
Corneal abrasion
A scratched or injured cornea. Symptoms include redness, watering, light sensitivity, foreign-body sensation
Can be dramatic or traumatic like being hit in the face or eye by something, or something as simple as rubbing an itchy eye or getting something out of their eye.
* If you end up with something in your eye, the best option is to flush it out with water or saline
Bacteria on your hands or the thing that scratched your eye can lead to a deeper infection, but most of the time, if you use caution, it will heal itself rather quickly.
**Solution for light sensitivity: wear sunglasses at night
Detached retina
When the retina detaches from the back of the eye. Sounds awful but it doesn’t hurt. The retina a web of nerves in the back of your eye that sends signals to the brain.
Closing curtain sensation is where part of the view of vision will become shadowed as the retina detaches gradually from one side to the other. Floaters also show up if this is happening. (All floaters ARE NOT related to the retina.)
Sudden detachment can be caused by head injuries or sudden intra-ocular pressure drops (the fluid pressure inside your eyeball). This sudden detachment is experienced as a flash of light and then sudden darkness. Sudden or gradual detachment requires immediate medical attention and can be repaired with surgery and medical intervention.
Diabetic retinopathy do to chronic damage can lead to retina detachment. *The risk of retina detachment occurring after an eye procedure (lasik surgery or cataracts surgery) is skewed for people with severe nearsightedness, possibly due to a genetic disposition of having a shorter retina.
Audience Question
Safe to use allergy eye drops long-term?
Answer: Sure! The only problem is that chronic use can lead to your body not responding to the same med over and over as well. So, to avoid this, swap between drops and allergy tabs – based on if you’re experiencing “eye only” allergies or a wider allergy response that involves the sinuses too.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Conditions 1 [Show Notes]

Eye Conditions in ABC order
Your eyes work together so that the line of focus for each eye cross, and that is your most in focus image. So as your eyes make tiny adjustments, you can focus on things close up or far away.
Amblyopia
If you have a lazy eye, the muscles don’t allow the eye to focus and coordinate with the strong eye. This can lead to double vision or blurry vision. I remember it because it sounds like “ambling” which can mean to meander or wander around. Versions of this can be caused by torticollis, where a baby’s head is tilted or twisted due to positioning in the womb. The eye can either compensate for the difference or it’ll just give up and let the dominant eye do all the work. Correction of this issue usually involves patching the strong eye and making the weak eye do all the work. The blurry or double vision can lead to headaches. Overuse and fatigue (like long days at work) can make it worse.
Astigmatism
An astigmatism no a stigmatism. It’s an irregularly-shaped cornea; think baseball vs football. A circular lens (baseball) focuses light to a single point. A football-shaped lens focuses light to a line, so that makes the vision blurry. This is why people with astigmatism will squint. Squinting is a way for your eyes to manipulate the amount of light coming in and alter the shape of the eye to clear up the image of what they’re looking at.
Lasix procedures can correct astigmatism – the laser does micro-damage to the eye and it heals more circular in the eye.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of eye lids. Can result in dry eye. It can affect the outside (eye lashes side) or the inside (lubrication gland size). This is NOT a stye. Caused by a chronic build-up of bacteria, skin flakes, dried eye lubrication. Some skin conditions can make a person more susceptible to blepharitis – Rosacea (overgrowth of skin bacteria), severe dermatitis, including psoriasis. It’s recommended to use really good eye hygiene before having a doctor intervene. Using warm compresses to keep dried skin and “eye crusties” soft and glands open so they don’t get clogged. Using clean cotton swabs or clothes instead of your hands to touch or wipe things out of your eyes, so you don’t transfer bacteria. Doctor’s can insert a catheter into the tear ducts to keep it open and less likely to keep it clogged. There’s not a cure to make it go away for good.
Cataracts
The lens of the eye gets cloudy due to proteins clumping up. People have described trying to see with cataracts like trying to look through wax paper. Risk of cataracts normally increases with age. The risk for cataracts can be increased even more by chronic diseases (diabetes, high blood pressure), poor health habits (obesity, smoking, alcohol use), long-term use of certain medications (steroids, hormone replacement therapy). The current treatment for cataracts is lens replacement. The old treatment would be just removing the proteins, but depending on a person’s longevity, they may get cataracts again in their lifetime.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Vitamins 2 [Show Notes]

Remember: if a vitamin is good for one place in your body, it’s probably good for a lot of places in your body. It’s a marketing ploy to call them eye vitamins.
Eye Vitamins
- Thiamine (B-1): thiamine is used heavily in your liver, to help metabolize alcohol. Most well-known deficiency in alcoholics. Thiamine also helps nerves produce several neurotransmitters, as well as protects your nerves from inflammatory chemicals (the chemicals in your body that trigger swelling and pain). You don’t want inflammation in your optical nerves. You also don’t want the signals from your eyes to your brain and back to be slow.
- Folic acid: important for pregnancy women and fetal development, deficiency can cause a type of anemia. It’s main job is to help make accurate copies of the DNA and RNA when cells are dividing and multiplying. You don’t want typos in your DNA! This is important for your eyes because the cells of your eyes is because they are some of the fastest reproducing and dividing cells in your body.
- Omega-3 Fatty acids: Beneficial for heart health, found in oils. Oils in your body are lubricating. Omega-3 fatty acids are building blocks for the cholesterol that is build into cell membranes that keep the fluid and slippery. The body also uses O3FA to produce the natural lubrication in your eye.
- N-Acetylcystine (NAC): an amino acid (building block of protein). Glutathione – your body’s naturally produced antioxidant. NAC is used when the cells build and store glutathione. Glutathione focuses mainly on oxygen-based free radicals.
- Alpha Lipoid Acid (ALA): another antioxidant. Found in sources of natural oils – seeds and nuts.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: 2 nutrients that are found in red, orange, and yellow fruits and vegetables (and that actually cause them to be those colors in the first place). Their main goal in your eyes are to prevent blue light damage. Blue light is a short wavelength with a higher speed and energy than the lower colors of light. This energetic light can damage cells in your eyes, so the orange nutrients blocks this energetic waves so you can still see the blue colors, but it’s more chill and doesn’t cause damage to the retina. These nutrients concentrate in the macula.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Vitamins 1 [Show Notes]

Eye Vitamins
- Vitamin C: helps make collagen, allows iron to be absorbed, and acts as a neurotransmitter co-factor (helps in the process of creating and sending messages).
- Vitamin E: antioxidant, it traps up free radicals so they don’t damage cells in important organs.
- Beta-Carotene: a pre-cursor to Vitamin A (this happens in your liver). Vitamin A works with proteins in your eyes to create light-sensitive molecules to aid in color vision and seeing in dim light.
- Zinc: helps Vitamin A know where it’s needed in the body and helps it get there.
- Selenium: helps the body absorb Vitamin E.
- Calcium: vital for muscle and nerve conduction (think electricity).
Bonus
Depending on what nutrient is missing to cause anemia, the red blood cells will have a certain appearance.
Some vitamins are fat soluble. They hang out in your adipose tissue, and can cause problems if you get them in too large amounts.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eye Anatomy [Show Notes]

Eyes
Your eyes are more complex than any camera on the planet!
Cornea: a concave lens on the front of your eye that focuses light
Iris: the colored part, a diaphragm that controls how much light comes in (the pupil is the hole the light enters = equivalent to the aperture of a camera)
Lens: the “focuser”, uses a process called accommodation to focus near to far and make the image as sharp and clear as possible
Retina: the sensor, and sends signals to the brain to translate light into an images
The retina has 2 types of sensors:
- Rods – detect light intensity
- Cones – color differentiation
Two special areas of the retina:
- Macula – right in the middle of the retina, they place that detects the most detail (that’s why the center of your vision field is a clearer picture than the periphery)
- Fovea – the center of the macula, it contains cones (color sensors) only to aid in the translation of very fine details
Support structures
- Extra-ocular muscles – allows your eyes to move around in their holes
- There are chambers of fluid that are between each structure of the eye, and that fluid helps hold nutrients that feed those parts, and remove waste
- Choroid: the layer that holds all the blood vessels that feed the eyes
- Sclera: the whites of your eyes, an outer coating that hold everything inside
- Conjuntiva: the mucus membrane that attaches the sclera to the eyelids; produces liquid for lubrication and trapping invaders
PSA
Please don’t vigorously rub or scratch your eyes, you could hurt them!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Brainstem

Brainstem Basics
Your brainstem is the most basic area of the brain. The area of the brain that we have in common with almost all other levels of the animal kingdom. It extends right into the spinal cord. A lot of other whole body involuntary reflexes come from the spinal cord – that’s another story for another day).
3 main parts
- Medulla oblongata – rhythm center (heart rate, breathing, swallowing, vomiting and coughing reflex) – they’re all involuntary
- Pons (not ponds) – the bridge between the cerebellum hemispheres and other brain regions, helps coordinate the right side and left side of your body for complex activities
- Midbrain – sensory reflexes (also involuntary) – blinking, eye focusing, pupil dilation in response to light, visual and auditory startling reflex that kick-starts the “fight or flight cascade”.
Other eye focusing problems are not rooted in the midbrain. They are more likely rooted in the areas of the brain that control orbital muscles or in the areas that translate what your eyes are seeing, like a “lazy eye” or drifting eye or being cross-eyed. There are therapies that doctors prescribe to try and strengthen the weak eye. Blinking is usually a response to eye moisture.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Blood Brain Barrier [Show Notes]

Basics
The blood brain barrier is the last layer of cells between what’s in your blood and the extracellular fluid around your brain cells.
You’re born with it! It’s main job is filtration.
2 ways things get through the blood brain barrier:
- Passive diffusion: small, neutral molecules (water, gases, lipid-soluble)
- Active transport: glucose, amino acids, drugs (like a revolving door)
Permeability: how easily something can pass through a layer without work
Things that change permeability:
- Inflammation – stretches layer and makes holes bigger (meningitis, injury)
- Multiple sclerosis – an auto-immune disease that can degrade the BBB
- Alzheimer’s – BBB becomes overwhelmed with antibodies and burns out
*Scary Section*
Rabies is a virus that is small and can get through the blood brain barrier but the immune system cells, antibodies from the vaccine, and medicines can’t.
HIV encephalopathy is caused when a mutation of the HIV gets into the brain and use brain cells to replicate (rather than the well-known T-cells of the immune system). There is also a rare symptom of HIV called HIV-associated dementia.
Callback
microchimerisms – Pregnancy causes the permeability of many areas of the body to change, and this includes the BBB.
Test Yourself
Drugs that have central nervous system effects (good) or side effects (bad) cross the BBB. See what you know of different medications and what job they’re supposed to do and what negative side effects they cause and see if you can guess if they cross the BBB.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Male DNA in the Female Brain

*Sorry again for crying baby*
Male DNA In The News
The news reported that scientists had discovered a link between male DNA found in the brain of the women who gave birth to sons.
Microchimerism = DNA fragment of another organism that incorporates into you
This particular microchimerism involves the Y chromosome (because otherwise, you wouldn’t know it was specifically male).
Other documented microchimerism studies have reason to believe they may be beneficial – especially in a process called immuno-surveillance (when the immune system is patrolling around looking for things that don’t belong there).
The blood brain barrier is the last layer of cells between what’s in your blood and your brain cells. DNA fragments are small and can easily pass through the BBB, especially during pregnancy when membrane permeability (the penetrable-ness) has increased all throughout the body already.
The primary resource written by the scientists that did the study of the female brains states that their findings were pretty much inconclusive – partly due to the small sample size of brains they had available. And they couldn’t study living people. They were mostly trying to decide if this male microchimerism had a positive or negative effect on Alzheimer’s risk. The final conclusion – we dunno. Another obstacle was that the complete health history of the samples they used was not known.
Other sources have stated hypotheses regarding the number of children a woman has and the risk of early onset Alzheimer’s.
This issue with reporting on studies like these is that Alzheimer’s has so many factors that may increase or decrease risk and science is pretty sure there’s NOT just one thing that will cause or prevent someone from developing this disease.
The only thing they could conclude is that microchimerisms are evolutionarily significant.
Here’s the primary journal article.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
An Accordion in Your Brain
Cerebellum Basics
Your cerebellum is a separate part of your brain that sits under the occipital lobe. It is responsible for unconscious motor functions, and is organized differently than the cerebrum. It is packed tightly together in neat folds like an accordion. And it has 3 lobes:
- Anterior (in the front) – it keeps the body visually “centered” and on balance, as well as moving the head or body to keep the eyes level with the horizon. Alcoholism can cause damage to this area that results in a person being sober but still walking “drunk”.
- Follcular-nodular (in the middle with nodules on it) – responsible for eye movement in response to motion. It is responsible for correcting balance based on signals from the body rather than the eyes. This is how you know you’re falling over when you have your eyes closed. Also responsible for muscle tone (aka the passive contraction or “readiness” of a relaxed muscle).
- Posterior (in the back) – responsible for fine motor coordination and it turns off signals for involuntary movements.
Purkinje cells are the main type of neuron in the cerebellum – SO BEAUTIFUL!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Now You See It [Show Notes]

Occipital Lobe Review
A brain lesion is a place in the brain that doesn’t fire when it should or fires sporadically when it shouldn’t. Occipital lobe lesions can lead to hallucinations that range from amorphous to extremely detailed.
Field blindness: a lesion causes the occipital lobe to not translate the information from one or more spots of the visual map (your whole view). Blind spots (round) or visual cuts (lines).
Photosensitivity seizures: seizures triggered by visual overstimulation. Even though stereotypical in different forms of entertainment, these only accounts for about 10% of seizure triggers. Seizures triggered by visual stimulation can range from mild to severe.
Certain types of blindness can be rooted in translation problems in the brain, rather than reception problems in the eyeball.
Lesions in the occipital-temporal-parietal junction:
- Color agnosia: can see the colors but can’t recall the names; simplified colors (all greens appear to be the same green)
- Movement agnosia: think weeping angels (things only move to a new position when you’re not looking at it) or moving items appear blurry
- Agraphia: unable to communicate in writin
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Eyes In The Back of Your Head [Show Notes]

Occipital Lobe Basics
The occipital lobe sits in the back of your head, it directly connects to your eyes.
2 Streams of messages that your eyes send to your occipital lobe.
- Ventral stream – translates “what”
- Dorsal stream – translates “where” and “how”
It sends translated information to the necessary part of the brain to respond or react to what you saw. This is how hand-eye coordination works (not just for athletes). And, since so much of the information we receive is visual means that the occipital lobe doesn’t do much else.
**The following is complete speculation based on my experiences as a Mom.**
Mom’s get accused of having eyes in the back of their head – but my guess is that mom’s gain a keener sense of spacial awareness regarding the things that are happening around you. Also, mom’s hearing become much more attuned to specific sounds (aka knowing their baby’s voice from other baby voices) to the point of knowing the difference between the sound of crayons coloring on paper versus crayons coloring on a wall!
If it hasn’t been obvious, let me just say that no part of the brain acts and reacts all by itself. Many of the complex activities we complete as humans involve many areas of the brain simultaneously or sequentially.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Art & Vitamins [Show Notes]
Temporal Lobe Problems
Temporal lobe lesions can lead to dyslexia.
Receptive aphasia: can’t receive or translate speech meaning
Word deafness: words are only noise
Temporal lobe lesions can also lead to deafness. The ears are fine, but the wires that translate input as sound are damaged. (Possibly what happened to Helen Keller).
Callbacks
Big Words
Prospoagnosia = facial blindness
Clinical apathy: you forget how to feel
Anterograde amnesia: can’t make new memories
Retrograde amnesia: can’t recall past memories
Situational amnesia: self-preservation from trauma
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
- Vitamin B-1 (Thiamine) deficiency
- alcoholics
- careless vegetarian/vegan diets
- Lose ability to walk, talk, and remember
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Seems like only yesterday [Show Notes]

Temporal Lobe Basics
The temporal lobe is located on each side of your head by your ears. It helps you process auditory input and identify sounds.
There is a special area called Wernicke’s area. It helps identify the meaning behind speech and vocal tones. This is different from Broca’s area, which is just able to identify some sounds as being words.
This is where your long-term memory lives, like facts and knowledge (declarative).
Emotionally charged memories are also held in the temporal lobe, but they have a special connection to the amygdala (which is part of the limbic system). These memories have a high level of detail, and usually can’t be recalled without also recalling the emotion. They also don’t have a sense of time.
Mind Games
Memories in the temporal lobe can lead to déjà vu.
The temporal lobe allows you to see a simple or incomplete image and fill in all sorts of details, whether it be the details of the image or a long train of connected memories.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Sugar for Brains [Show Notes]
Sugar Basics
Sugar in your blood = glucose
Your body prefers glucose over any other sugar out there.
-ose = sugar suffix
GlucOSE
FructOSE – fruit sugar
SucrOSE – table sugar
SucralOSE – Splenda
Your body can turn any of these other sugars in to glucose. It can actually turn other carbohydrates, and even non-sugar molecules into glucose if it really needs to. This all happens in your liver…
If you were in a long-term starvation or malnutrition situation, your body would circulate non-glucose energy sources to try to get energy, since the process of making glucose can be relatively slow. This is because your body would prefer to live than die.
Brain Food
The brain is a picky eater, and refuses to utilize non-glucose sources of energy. This is because your brain works A LOT! And it doesn’t have time to use inefficient sources of energy. Therefore, it will hog the glucose from the rest of your body.
Your skeletal muscles use glucose to do work. This is why people with diabetes have to be extra cautious when they exercise.
Extra glucose gets saved for those times when you’re not eating. It gets put in a really long chain called glycogen. But getting the glucose back from the glycogen can be relatively slow.
Recovering from an episode of low blood sugar takes time and requires rest (so you’re not burning through the fuel as fast as you replenish it). But it can also be emotionally stressful because you may be required to eat “unhealthy” amounts of sugary or carb-heavy foods to get back to normal.
Energy Production
Glucose has a very complex metabolism cycle – the Krebs cycle.
One intermediate is glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) – there is a genetic mutation where a protein for this step doesn’t do it’s job very well. If this step gets delayed or clogged up, then there is a detour metabolism step that leads to triglyceride production, when then leads to fat storage. *womp womp* (note: triglycerides are useful in the right amounts for cell repair) This is also why eating large amounts of sugary plus fatty foods can lead to quick weight gain.
The end result of this cycle is Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). It is super energetic when a phosphate piece is removed. It’s like the body’s dynamite. This is how a sugar high works – all the sugar leads to all the dynamite exploding at once, but then it takes a while for it to get replenished, and that’s why you crash after a sugar-high.
Low Blood Sugar is Bad
To immediately recover from low blood sugar, you need simple sugar (orange juice, regular soda, sugar-full hard candy, glucose tabs or paste or gel). To continue to recover, you need carbs plus something that will help it not absorb so fast (i.e. protein, healthy fats).
If you ever look at the underside of your tongue, you can see the blood vessels really clearly because they’re really close to the surface. So if someone is unconscious due to low blood sugar, you can use a glucose tablet or gel under their tongue and it will absorb into the blood stream. This is also how you can absorb sugar quickly from sugar-full gum.
Low blood sugar can lead to emotional fluctuations (aka crabby and grouchy) and short-term memory loss (and not just because you passed out).
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Brain Lesions [Show Notes]
Basics
Brain lesion = a group of brain cells that look different from surrounding cells on a brain scan
Dark lesions – an area where the brain cells are missing or an area where signal is not firing (damaged cells)
Light lesions – an area where the signals are firing at the wrong times (like a shorted out wire). Seizure – when the brain fires the electricity at the wrong time.
Lesions around the brain
A lesion in the Parietal lobe could affect how the body translates sensations (i.e. pain). These lesions are usually caused by injury or stroke.
If there is a lesion in the optical lobe of the brain (the area that “sees” what your eyes are looking at), then the signals from the eyes may not come through, and therefore the parietal cannot help map what you were looking at once it’s not there anymore.
Sensory seizures – feeling things on you or touching you that aren’t really there. (unsure if this is related to the auras that come before migraines). No medication necessary.
Extinction phenomenon: thinking that a sensation stopped before it really did. You body can’t translate two messages of the same type at the same time. Like when you try to locate the same place on each side of your body (i.e. making pigtails even).
Some Big Words
Dyslexia: can be related to written language, spoken language, or any other message being translated as language
Dysphasia or Aphasia: mixed up or missing words
Dyscalculia: it’s hard to math. Difficulty estimating distances, spacial mapping, and time passage. Dana White of A Slob Comes Clean talks about TPAD (Time Passage Awareness Disorder)
Apraxia: unable plan what you want your body to do in order to make your body do it. The deeper the path the more “natural” the action is. Muscle memory is just an extremely well-developed motor path, so that you can even not do that action for a while, and when you do it again, you don’t have to “relearn” it. If this is caused by a stroke, therapy can help try and re-route the information. Apraxia can affect gross motor movements (large movements with your body) – aka global apraxia, or it can affect speech motor planning.
Gerstmann Syndrome: no motor path to write, or math, or to feel and use your fingers as separate digits. Also involves a left-right mix up. In adults, it’s the results of a stroke. In kids, they have not a clue. Therapy can help kids get past the motor issues, but not the mathing issues.
Constructional apraxia: know how blocks should fit together, but the brain can’t make their body build it.
Dressing apraxia: know how clothes should be worn and where it goes, but the brain can’t make the body dress itself. This shows up in dementia and Alzheimer’s a lot.
Amorphosynthesis – your brain is not aware of some part of your body. Usually a symptom after as stroke.
Another symptom of a stroke is when a person is unaware of one-half of their visual field. So they will only write on one half of the paper (the half they can see) or read only one half of the page of a book.
Anosognosia – a person is not aware that they have a disorder, disease, or disability. This is not just denial. The area of their brain that would recognize “I’m sick” or “I’m hurt” doesn’t work.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Health Story: Emily Olsen

Takeaway point
Talk to the people at the practice at which you are wanting to start receiving care. If the doctor is not available for a direct interview, the office manager may be able to answer questions regarding the practitioners and their style of communicating with patients and their approach to care.
Connect with Emily
You can contact Emily at WholeLifeWellness.co (CO not COM) – it is under construction.
You can find out information about the Whole Foods Nutrition Challenge on her Facebook page: facebook.com/wholelifewellness3.
Contact her at: https://www.facebook.com/wholelifewellness3
As promised – The 7-Day Whole Food Challenge – sign up for FREE!!!
***The next challenge starts January 9, 2017!***
***Time Sensitive****
She’s offering some AWESOME specials–good until November 30th!
Here are the details (but be sure to watch the video for further explanations!):
*One-on-one 6-month coaching program: $584.00 (a 41% discount from $990.00–in honor of my 41st birthday!)
*The ‘It’s About Time! Wellness for Work’ 60-Day course–a nitty-gritty and encouraging course focusing on being your best self for your best work and vocation (starting on Dec 5th): 194.00
*’Consistency ‘Til Christmas’–a 25-day engaging group accountability experience–focusing on water, steps, veggies, and sleep–in order to stay healthy and focused during the holiday season (starting on Dec 1): $25
She’s offering some AWESOME specials–good until November 30th!
Here are the details (but be sure to watch the video for further explanations!):
*One-on-one 6-month coaching program: $584.00 (a 41% discount from $990.00–in honor of my 41st birthday!)
*The ‘It’s About Time! Wellness for Work’ 60-Day course–a nitty-gritty and encouraging course focusing on being your best self for your best work and vocation (starting on Dec 5th): 194.00
*’Consistency ‘Til Christmas’–a 25-day engaging group accountability experience–focusing on water, steps, veggies, and sleep–in order to stay healthy and focused during the holiday season (starting on Dec 1): $25
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
See it in my head [Show Notes]

Parietal Lobe
It sits in the top of your head
- Responsible for translating: touch, temperature, and pain.
- So does it tickle? Or hurt? How does it hurt – throbbing, stabbing, sharp, dull?
The way your body translates temperature is based on the relative temperature to the body part that is being touched.
- So does it tickle? Or hurt? How does it hurt – throbbing, stabbing, sharp, dull?
- Proprioception – ability to know where you are in space relative to the other things around you
- That awkward moment when you think the toilet is higher or closer that it really is and you almost fall.
- Hand-eye coordination – being able to see something that is moving and make your body to interact with it.
- Two-point discrimination – the body’s ability to tell if it’s being touched by one thing or two separate things. Different parts of your body have different levels of sensitivity. Large body parts have a larger distance than small body parts (fingers and tongue have the closest discrimination distance due to the number of sensors).
- Graphesthesia = writing feelings = being able to correctly translate letters or shapes drawn on your body without you looking.
When someone says “I can see it in my head” – it’s the area that can recall visual memories. Remembering the last place you saw your keys or visualizing driving directions based on the landmarks you pass (which is the only way we give directions in the South). So, when someone closes their eyes to try and remember something, they’re trying to deactivate their eyes and activate the parietal lobe.
Being able to identify a 3D object with your hands by touch only, and without your eyes. This is also how Braille works, the dot patterns created to represent letters.
Good info here and here about Braille activates the brain.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
On the tip of my brain [Show Notes]

Recap
Frontal Lobe
- Motor cortex – voluntary muscle movements, including the muscles that control speech
- Language translation
- Prefrontal cortex – personality, judgment
Dopamine
The main chemical, or neurotransmitter, that functions in the frontal lobe is dopamine.
Reward System and Addiction
- Dopamine is part of your brain’s reward system.
- So think about when you get a Facebook notification…. dopamine is released in your brain, and your brain really likes how dopamine makes it feel. Feels good! So you’re brain will help you pay more attention to the things that will get you more dopamine (that’s why a 5-second Facebook glance can turn into 30 minutes). This also means that dopamine is involved in your attention span.
- Some newer studies are looking at dopamine’s effect on addiction.
- The problem is that it requires increasing levels of “excitement” for your brain to receive the same level of dopamine as the very first time. This is why people with devastating addictions end up on a downward spiral of ruin.
Memories
- Dopamine is also involved in short-term memory, especially in complex or cascading tasks (where you have to remember a thing from Step A to complete Step B) in your prefrontal cortex.
- Diseases that take away short-term memory: Dementia (general or Parkinson’s-related), Alzheimers.
- Dopamine is being studied in how it related to dementia and Alzheimer’s. It’s effects are already known in Parkinson’s disease.
- To form memories, your brain has to access the same information over and over again (like a smooth, speedy highway). A road only traveled once, is not easy to travel again, especially if there’s a long period of time between trips down that road. So in diseases that involve brain cell death, there becomes less and less routes to take to the same memory. Thus, the older memories are the last to go because they have the most access routes.
Planing
- Dopamine is responsible for your planning and motivation mechanisms. If I make a plan and carry out the plan, the reward of dopamine is the outcome.
A New Discovery
They’ve discovered a genetic component that affects the shape of the dopamine receptors.
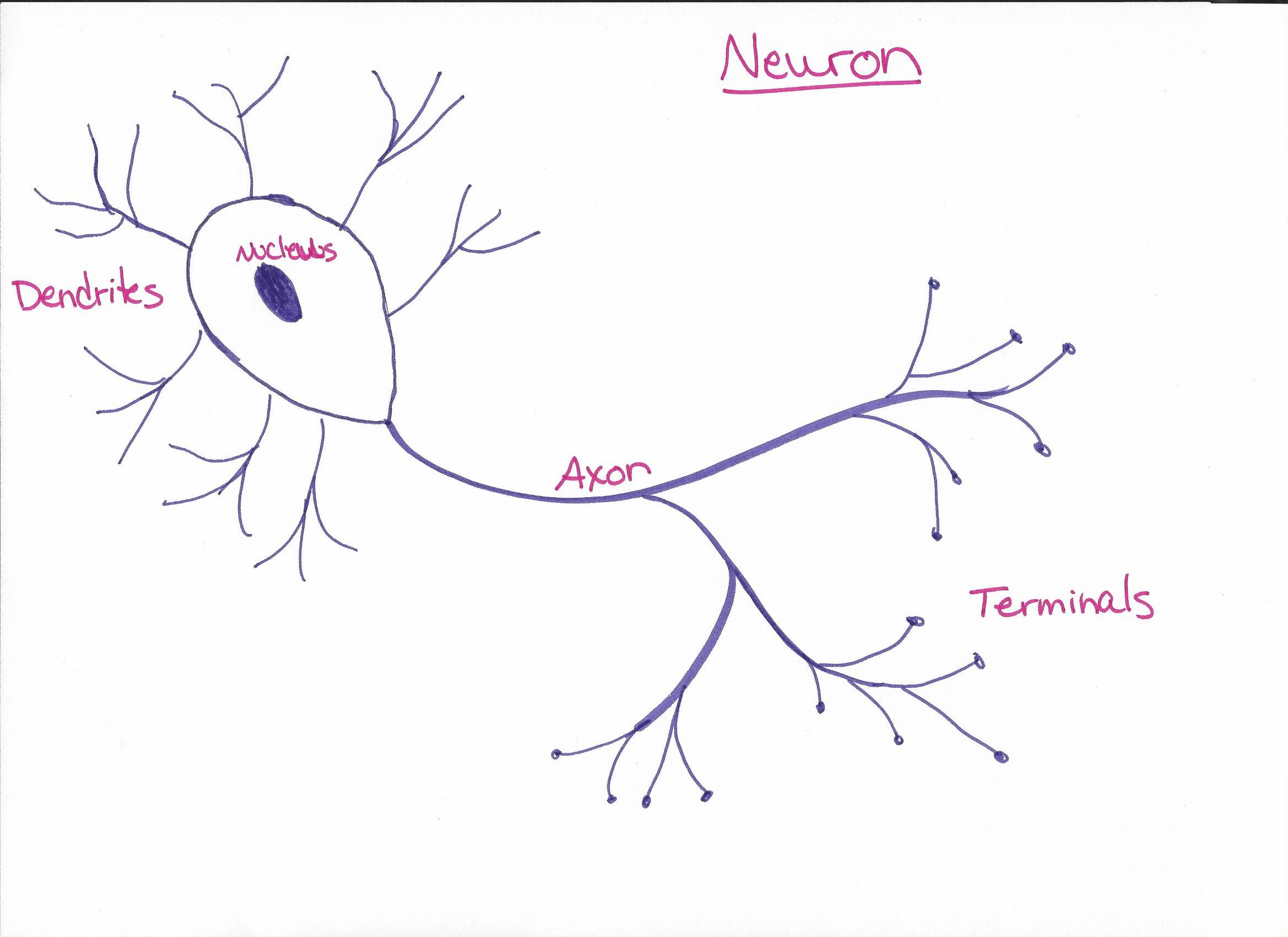
These cells in your brain don’t actually touch each other. The terminals spit out dopamine, and it floats in the space and hopefully comes in contact with the next cell’s dendrites. The dendrites have dopamine-shaped keyholes, and the dopamine should fit in the keyholes perfectly. But they have discovered that a genetic component affects the keyhole shapes, and this make be a root cause for schizophrenia and attention deficits.
If you think about it, the classic symptoms of schizophrenia – paranoia, anxiety, hallucinations, split personalities – most things affected in your prefrontal cortex. So if the dopamine receptors are “broken” in this area of your frontal lobe, you can see how there could be a dysfunction. And this is produced at the genetic level. Science is still learning about this…
Stroke
Strokes or brain injury in this area of your brain can affect personality. These parts of your brain don’t grow back! Some issues related to the speech motor area of the brain (Broca’s area). Stuttering (clinically diagnosed) is a misfire in the motor planning part of speech. Aphasia (loss of words) – part of you brain knows the word but you can’t seem to get it out of your mouth. Strokes in this area can cause some strange effects in the loss of words.
Seizures
There is also a type of epilepsy (seizures). Seizures are a misfire or a short in the electrical signals of the brain. Seizures in the frontal lobe can possibly affect memory (epilepsy-related amnesia). Must be diagnosed by a neurologist.
Story Time
Back in the day, there was a guy named Pheneas Gage who worked on the railroad. An accident involving dynamite and a railroad spike, led to a major head injury and an altered personality!
We rub our forehead when we’re trying to remember something because that’s where our short-term memory is.
#RealTalk
Cynthia doesn’t have that many Facebook friends!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Makes You Who You Are [Show Notes]
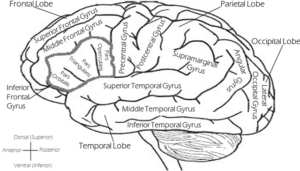
**Many apologies for the screaming baby***
Basics
Frontal Lobe – in the front of the brain (behind your forehead)
This is the area that contains your personality. A stroke or brain injury or damage can alter someone’s personality drastically.
We take personality tests, but they are too basic to take such a complex part of you and put it in a quadrant or on a spectrum.
This area of the brain is also well-connected to the limbic system (emotional center), and if those connections are broken through stroke or injury, then that causes personality changes too.
Frontal Lobe
- Motor cortex: voluntary muscle movements = how you choose to move your body.
- Prefrontal cortex: personality, complex cognitive behavior, decision-making, social behavior, judgment (not existential judgement – but simple things like opposites) – if this gets damaged in adults (so less chance to relearn things as kids would), they don’t sense the dread of the consequences of doing “bad” behaviors, thus they can live lifestyles that include sex, drugs, and crime.
- Broca’s area (confirmed: he was French): speech, language production, translation (not just audible language, but any type of symbol or gesture that would have meaning)
- stuttering and aphasia originate here
* This area of the brain doesn’t reach full development until almost 30 years old —> Insert rant here!!
Story Time
During the Heroic Era of medicine (not a well-named era) – they invented the Lobotomy – mainly trying to find a treatment for mental illnesses. Society was ok with doctors experimenting on criminals in prison and patients who were put in asylums by their families. It did cause changes in the people, thus they claimed the “cured” them.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
White Matter Matters [Show Notes]
Review
Disease like Alzheimer’s and dementia are grey matter issues – the creation and translation of messages are interrupted or dysfunctional. White matter is like the power cords that are responsible for sending the signals.
White matter diseases
- Hypomylenation – cells are created with a low amount of myelin; premature, chromosome-linked defects
- Cell Biology review: animal cells have a membrane and a nucleus that holds all the DNA, and cytoplasm, and then all the organelles that have different jobs – just like a self-contained factory. Some systems can be dysfunctional and the cell still live and replicate.
- Dysmylenation – neurodystrophy (a huge list based on what’s broken)
- Lysosomes – stores enzymes for breakdown
- Perioxosomes – stores enzymes for energy metabolism
- Mitochondrial – dysfunction of energy usage
- Amino acid metabolism dysfunction
- Demylenation
- Inflammatory: Multiple Sclerosis = autoimmune disease. The brain wants the body to do something but the message doesn’t make it to the body, so the body doesn’t move or has very jerky, irregular movements. Tests for antibodies can identify MS. Available treatment is mostly immune suppressants.
- Huntington’s is a genetic disease that presents in the same way. It has a very sad prognosis and presents in females starting between the ages of 30 and 50. Thus they have already planned a life and possibly had kids who now may have the same disease. Genetic testing can identify Huntington’s.
- Viral – PML (Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy); J-virus a typical virus that may mutate and go dormant in the brain. If the immune system is lowered drastically – due to suppression or immunodeficiency diseases, this virus will wake up and attack the myelin of the neurons.
- Acquired metabolism demyleniation (being exposed to chemicals) – “Chasing the Dragon” – refers to a technique used to keep melted pills from burning in a container (usually a spoon) while it’s being heated by a flame from underneath and the vapors are inhaled. Drug of choice: heroin. **DON’T DO DRUGS**
- Hypoxic ischemic – loss of oxygen. Examples: asphyxiation, drowning, ischemic stroke.
- Mechanical – compression due to injury or swelling
Call Back
Migraines are not a white matter issue, they are a brain chemistry issue. Learn more on the Headache episode
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Where has all the grey matter gone [Show Notes]

Review
Grey matter – neuron cell bodies that create and translate messages
White matter – myelin-covered axons that transmits the messages across the brain
Conditions that affect grey matter
- Dementia – memory starts to fail with age (due to the death of brain cells). Newest formed memories get lost first (Last In First Out), and it progresses until the vital functions are lost.
- Alzheimer’s – similar results as dementia, different cause.
- Bipolar – there is not a clear explanation, but the grey matter of someone who exhibits bipolar symptoms looks different on a brain scan from the grey matter of someone who doesn’t.
- Amnesia – can be because the cells holding the information or memories have been injured or killed due to injury, or because the wires that would send the messages for recall have been damaged. This can be caused by head injuries. In traumatic experiences, amnesia is a self-preserving mechanism.
- Lewy- body dementia – a type of dementia that manifests in Parkinson’s disease. As a neuron cell dies, it fills up with protein and blocks message transmission. These large clumps of protein-filled cells will show on a brain scan. These buildups can lead to hallucinations – visual or auditory. Also, affects memories, just like typical dementia does.
- Schizophrenia – stereotypical symptoms can be caused by changes in grey matter, but not the same as protein build-up. And still a lot unknown about why.
Your brain cells do not reproduce and replenish the way other cells (like your skin) do. We do know that the brain can create new cells, but it is a very slow process that requires very specific conditions to be present. But the new growth of brain cells is not fast enough to slow or reverse a disease.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Wrinkly Brain [Show Notes]

Brain Basics
All brains are wrinkly. Wrinkles in your brain are a good thing. Wrinkles are biology’s way of maximizing surface area while conserving space.
The plateaus of the brain are called gyri (or a gyrus).
The smaller, sunken in wrinkles are called sulci (or a sulcus). Sunken in sulci – that’s how I remember it.
The larger canyons of the brain are called fissures. These are the groves that separate the hemispheres and the lobes of the brain.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
White matter vs Grey Matter [Show Notes]

Basic Brain Biology
Your brain is made of cells. Those cells are called neurons. Neurons transmit signals in the form of electricity (aka .positive and negative charges). One end of a neuron will build a signal or charge, and once it reaches a certain threshold, then a signal is send down the axons.
Most of the cells in your body touch and transmit signals and pass chemicals through their membranes. Neurons do not touch. The terminals of one will get really really close to the dendrites of another.
They’re really good at the telephone game – mostly because the body tries to minimize the number of neurons involved in passing a signal.
Axons are coated in myelin. Myelin insulates the axon that helps the signal being sent travel faster, and prevents it from getting lost to something else touching it. You want the signal to have to same strength when it reaches its destination as it did when it left its source.
Parts of a neuron
Dendrites: receives signals from previous neuron
Cell body: contains the nucleus and creates and translates signals
Axon: the “wire” that transmits signals
Terminals: sends signals to the next neuron
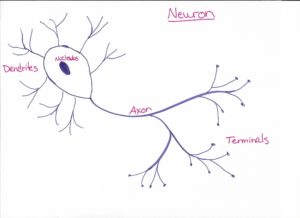
Grey matter – cell bodies, dendrites, and terminals
White matter – axons wrapped in myelin
Grey matter – information storage and translation
White matter – information transmission
Brain: grey matter is on the outside, white matter is on the inside
Spinal cord: grey matter is on the inside, white matter is on the outside.
PS. Grey? Gray? IDK!!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Meningitis [Show Notes]

Basics
Meningitis = inflammation of meninges
Generalized symptoms: fever, headache, stiff neck, light sensitivity, confusion, lethargy,
4 types of infectious meningitis
- Bacterial – we have a vaccine for that! 3-7 days; spreads in close communities (like college dorms). Spreads through prolonged contact. Confirmed through spinal tap and cerebrospinal fluid culture
- Viral – most common type; can be caused by lots of viruses: enterovirus, mumps, measles, flu, west nile. 7-10 days. This is why I believe in vaccines!
- Fungal – not contagious; most common in patient with suppressed immune systems or secondary from surgery.
- Parasitic – Rare yet fatal. Amoeba enters through nose from warm contaminated fresh water sources or pool, even hot springs (warm up to 115* F). Only 31 cases in the 10 years between 2002 and 2012. Destroys brain tissue ~ 5 days.
Non-infectious causes: Surgery, injury, lupus, cancer
The most important thing is that all of this be monitored by a doctor – ALWAYS!!
2 quick tests for meningitis
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Special Episode #4: Life & Blood Sugar [Show Notes]

For someone with diabetes, everything they do in life affects their blood sugar. They could be eating 100% right and taking their medicine 100% right, and something would cause the blood sugar to be off.
Exercise
It is well-accepted that exercise is good for you. Your body will store extra sugar as a large molecule called Glycogen. Imagine a line of kindergarteners hold hands trying to make it through the museum, Glycogen is just a bunch of glucoses holding hands. When you’re not eating, your body will snip off a glucose at a time as it needs it. The liver stores and directs the glycogen most of the time. Your skeletal muscles also store some glycogen, because when they do work (i.e. exercise), it takes too long for the liver to snip off glucose from glycogen and send it to them.
After exercise, the body replenishes the muscles’ glycogen stores. This can cause the blood sugar level to drop, for someone with diabetes, this can be dangerous because they can’t “untake” medicine. When protein and carbohydrates are eaten together, before or after exercise, the blood sugar changes can happen more slowly – the nutrient absorption in the gut causes a “traffic jam” of sorts.
Sleep
Certain metabolism processes happen only when you sleep. Some people with diabetes wake up with really high blood sugar, others wake up with really low blood sugar. Sleep is not restful and restorative if the blood sugar is out of balance, but also if sleep is not restful, then blood sugar levels can be jacked up – not just in the morning, but for the rest of the day.
Stress
The hormones that are triggered by stress – even something as basic as adrenaline, can cause the body to respond to insulin and glucose differently.
Sickness
Your body is going to responds things differently when the immune system is in high gear – that includes insulin, glucose, the food you eat. An infection requires an antibiotic because you are infected with a bacteria. Bacteria are living organisms. Living organisms consume energy sources and produce waste. This can affect the sugar levels in your bloodstream. You’re immune system doing work also burns sugar.
Allergies
Works about the same as sickness. Your immune system is actively trying to protect you from something (allergens) and so it responds differently.
Smoking
If you smoke, STOP! The nicotine and other chemicals make you more resistant to insulin. This is most troublesome in Type 2 Diabetes.
Hormones
Especially for women, hormone cycles can affect sensitivity to insulin differently during different times of the month. Adrenaline can override almost any response to any previous hormone response.
Life is hard
Life with diabetes is super hard. Diabetes and other chronic diseases are silent and it doesn’t show on the outside at first sight. Extend grace, extend compassion.
The Nashville chapter of JDRF is having their annual One Walk on September 24th. Friend of the show and previous guest, Rachel Mayo has been #T1D for over 10 years and she is passionate about the cutting edge research and support JDRF provides for people and their families. Her goal is for her team to raise $5000, you can contribute!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Brain Bleeds [Show Notes]

Review
Your brain is held inside your skull by a tri-layer membrane called the meninges. These membranes and all the other structures in your brain are nourished by blood vessels, and different circumstances will make these vessels at risk of rupturing.
*ALL BRAIN BLEEDS REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION!*
Brain bleeds are classified based on the membrane they are closest to. They can be caused by physiological malformations, stroke or aneurism from age or disease, or trauma.
From the outside in
- Extracranial bleed: (extra = external; cranial = cranium = skull bones), between your skin and your skull. Doesn’t affect your brain, there is more room for it to stretch.
- Intracranial bleed: (intra = internal); bleeds inside the skull increase the intracranial pressure and requires medical intervention. Main goal is to reduce intracranial pressure so brain cells aren’t pressed on and damaged.
- Epidural (yep, that place they put the anesthesia for women having babies, except it’s in the spinal cord): Epi = above, Dural = Dura mater, that topmost, durable layer of the meninges. Between the skull and the dura mater.
- Subdural: Sub = under; blood leaks in between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater, which are normally in close contact, so the separation causes pain.
- Subarachnoid: under the arachnoid mater. Normally, under the arachnoid layer is the subarachnoid space which contain cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). People who have had a subarachnoid bleed and survived, describe hearing a “thunderclap”. Officially called a “thunderclap headache”. It’s like they can hear the blood vessel pop and experience extreme pain all over their head all at once. Described as “the worst headache of my entire life”. Because the pia mater under the subarachnoid space lays directly on top of the brain cells and follows all the grooves and wrinkles of the brain, this type of bleed will require emergent attention and possible surgery.
- Intracerebral: cerebral = cerebrum, the main part of your brain
- Intraparenchymal: Parenchyma = organ tissue, means it’s right up against the brain cells
- Intraventricular: Ventricles = pockets inside the brain that make, hold, and reabsorb CSF. The deepest part of the brain.
*ALL BRAIN BLEEDS REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION!*
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Special Episode #3: Meds & Blood Sugar

People with chronic diseases don’t get holidays or vacations from their medication.
4 ways medication can affect blood sugar
Type of medication
The goal of the medication that people with diabetes take is to lower blood sugar – either by increasing insulin sensitivity, encouraging the pancreas to make more insulin, or to replace insulin that’s not naturally made anymore. Metformin is like insulin’s wingman; it helps make the cells ready for insulin when it comes by. So usually these medications (including insulin) will lower blood glucose no matter if you eat or not.
Timing of medication
Most of the medications should not be taken if a meal is going to be skipped.
Dose of medication
The more sugar you eat, the more insulin you need. The higher the blood sugar level, the higher the dose is needed. It needs to stay proportional. Any form of sugar you eat gets turns into glucose, the complexity of the sugar determines how fast it raises your blood sugar. Even diabetics are at risk for hypoglycemia. If one little thing gets out of whack, it can cause a drop in blood sugar and require a “rescue”. Favorite hypoglycemia rescue “go to” is orange juice (lots of simple sugars). Regular soda can be used, as well as hard candy or glucose tablets. NO DIET SODA – artificial sweeteners do not affect sugar enough. High blood sugar can cause coma, lower blood sugar can cause coma. Bottom line: Coma is bad.
Interaction with medication
Fluoroquinolones can causes changes in blood sugar control and require a person to check their levels and adjust their medicines more often. Steroids can also cause blood sugar to be more uncontrolled – this is true for acute (short term) use or chronic (long term – like autoimmune diseases) use. Beta blockers used for blood pressure control can mask the symptoms of low blood sugar because the symptoms are very similar. Symptoms of low blood pressure: tiredness, weakness, dizziness, shakiness, inability to focus. The only way to know which one you’re experiencing is to check your blood sugar and your blood pressure.
The Nashville chapter of JDRF is having their annual One Walk on September 24th. Friend of the show and previous guest, Rachel Mayo has been #T1D for over 10 years and she is passionate about the cutting edge research and support JDRF provides for people and their families. Her goal is for her team to raise $5000, you can contribute!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Membranes [Show Notes]

Membranes Basics
Meninges are a triple-layer membrane that helps hold your brain in place.
The inside of your skull bones have many boney processes protruding out. The meninges surround the brain and provide a cushioning layer around it, and anchor to these processes. This allows the brain to be suspended inside the skull and not touch the top, sides, or bottom.
This setup is partly contributes to concussions. When the head experiences a large enough impact, the suspended brain crashes into the bone of the skull.
Meninges encase your brain and spinal cord to protect them.
Three layers
- Dura mater (mah-ter, not may-ter): durable and thick, contains large blood vessels. This is the layer that anchors directly to the skull bones. Membrane that divides hemispheres, separates a few lobes, and coats glands near the brain.
- Arachnoid mater (yes, like spiders): wispy like spider webs – thin & transparent. Directly in contact with Dura mater, but has cellular pillars that connect it to the Pia mater. The cerebrospinal fluid flows around these pillars. Also overs the outside of the part of the brain as a whole.
- Pia mater – delicate, contains the capillaries that nourish the brain. Is in direct contact with brain cells – following all the contours and wrinkles of the brain.
Subarachnoid space – hold cerebrospinal fluid (a closed fluid system that insulates and cushions the brain and spinal cord). Doesn’t mix with blood or lymph system.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Special Episode #2: Food & Blood Sugar

Blood Sugar Basics
Your blood sugar affects how tired you are, your productivity, and your moods. This is 1000x more true for those with diabetes.
Hypoglycemia = Low blood sugar
3 main energy sources in your food
Carbohydrates are some complex form of sugar that your body can turn into glucose very quickly. Glucose is the main form of sugar that your body uses for energy. Because your liver is very efficient in this process, you can get a blood sugar spike (sugar high) and then you crash after it’s over. Insulin is the key to the door to let the glucose in your cells.
Fats can be turned into sugar by your liver is your glucose stores are depleted. So, this can affect your blood sugar levels, although it’s less of an impact that carbohydrates. Insulin has another job – fat storage. If there’s a lot of fat, the insulin is being used up storing fat rather than allowing glucose into cells.
Proteins are promoted as a counterbalance to the carbs. It causes a traffic jam in the absorption and metabolism processes that allows the sugars into the blood stream much slower. The liver does have a process called gluconeogenesis (the creation of new sugar) where it can make sugar out of protein, but it’s a last resort.
Other things in your food
There is some evidence that shows caffeine causes temporary insulin resistance while it’s in the body. You still get an “energized” feeling b/c caffeine increases the heart rate but the energy usage is not very efficient because the glucose is not being used well.
Alcohol can drop your blood sugar initially, especially if it’s consumed on an empty stomach. When the liver is steadily detoxing the alcohol out of your bloodstream, the replenishment of the glucose supply slows down. This contributes to what make you feel sleepy after drinking alcohol. On the flip side, it will increase your blood sugar because 1) alcohol is usually mixed in a sugary drink (i.e. cocktails) and 2) alcohol is distilled from “high carb” sources (grapes, wheat, barley, rye, corn, etc).
Any changes to eating habits need to be exactly that – new habits. It can’t just be a program that you do once without permanent change. If you’re cutting out all or most of one of the 3 main energy sources, you have to make sure you keep up with your caloric needs.
Calorie Math
1 g of Fat = 9 calories
1 g of Carb = 4 calories
1 g of Protein = 3 calories
Calories are calories when it comes it energy, so the other nutrients from your foods are a more important to consider when choosing what to eat.
There are lots of things your body would have to adjust to when changing eating habits (digestion adjustments, for one) and 30 days may not be enough to get it “normalized”.
JDRF
The Nashville chapter of JDRF is having their annual One Walk on September 24th. Friend of the show and previous guest, Rachel Mayo has been #T1D for over 10 years and she is passionate about the cutting edge research and support JDRF provides for people and their families. Her goal is for her team to raise $5000, you can contribute!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credit: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Headache [Show Notes]

5 Types of Headaches
Tension Headache
They come on if you’re stressed or having to hold your body in an uncomfortable or unnatural position. Neck and shoulder tension can cause the headache to hurt in the back of your head (and can radiate to your eyes due to the location of the optic area of the brain). Intense facial expressions (including crying) can hurt in the front or sides of your head. Obsessive personality types are more prone to tension headaches. OTC pain meds help turn off pain receptors. Using a warm compress to loosen and soften muscles and then doing stretches can relax the muscles and relieve tension. Some people find that ice packs can help because the cold decreases the inflammation in the area that is tense and painful.
Cluster Headaches
They happen in groups or cycles. Mild to moderate pain. One-sided headache accompanied by watery eyes, sinus pressure, and runny nose on that same side. Don’t be fooled into thinking that it’s a sinus headache. The pain from cluster headaches will make you restless – “If I can just stay busy, I won’t think about the pain and will be ok”. This type of headache can be treated with OTC medications.
Sinus Headache
Your sinuses (tunnels in your head and face bones) are lined with mucous membranes. They can become inflamed if they are fighting off a virus (cold), infected by bacteria (sinus infection), or from overproduction due to a severe allergy attack. The inflammation, in itself, can cause pain. But if they swell shut and the air inside can’t even out pressure with the outside (just like your ears when you change altitude), it can cause pain. Antihistamines and decongestants can help, and again, OTC pain relievers.
Rebound Headache
If you use a medication for a prolonged period of time, your body chemistry will adjust to it always being there. So, if you stop taking it, your body notices the gap and responds by sending pain signals. This happens with headache medications as well as other pain medications. Can be an indication of medication overuse.
Migraine
These must meet a specific set of criteria to be diagnosed. And because they are most affected by brain chemistry, OTC medications rarely work, thus require prescription medications.
Diagnosis criteria
- 5 or more debilitating episodes
- An episode lasts 4-72 hrs
- At least 2 of the following:
- one-sided
- throbbing (feel the pulse or heartbeat)
- Moderate to severe
- Interferes or prohibits daily activity
- Daily activity makes it worse
- Sensitivity to light and/or sound
- With or without aura (visual disturbances – halo, floaters; hand numbness)
A deeper look
If your brain knows something is going on, it may preemptively redirect blood and nutrients to the vital organs and thus your extremities get neglected.
Still not 100% sure what causes migraines, Neurologists can do brain scans to look for patterns in electrical signals and misfirings. So far, we know it has something to do with neurotransmitters.
Hormones can affect the brain chemistry so strongly, that each menstrual cycle can come with migraine. Pregnancy hormones can cause migraines – either temporarily or permanently.
Serotonin, which is your “happy” chemical, is produced when your eyes are stimulated by sunlight. If it gets out of balance, the brain responds.
Treatment Options
- Triptans (a class of medications used to treat migraines) affect serotonin levels to try and rebalance it.
- OTC and home remedies don’t work for true migraines.
- Some people do get relief with ice packs. Ice reduces any inflammation, and also numbs the nerves so they don’t feel as much pain. **Ice must be used conservatively because too much ice contact can damage the skin**
- Other people find that warm compresses hurts because the muscles around the painful area get tense and the warmth can help them relax.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credit: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Headbone [Show Notes]
Headbones Basics
Your skull is made up of 22 bones. 2/3 of it consists of cranial bones, even though there are only 8 of them. The other 1/3 is your face.
Two main goals of the cranial bones: protects your brain, acts as an anchor for neck and face muscles.
The 8 bones are connected together by sutures (because they look like they’ve been sewn together) – and it is a tight fuse that doesn’t allow anything through.
The frontal bone – at your forehead, it’s on the FRONT. When babies are born, this bone is actually in 2 pieces to allow baby’s head to smush during delivery. It fuses together so tightly, that it becomes one bone by eight years old.
Fontanels = soft spots that babies have that allows for rapid brain and head growth. Babies have 6 total soft spots. All of them close up by 3 months old except the big one in the front.
Steve’s Story
His daughter’s soft spot would sink in and she would cry. His mother-in-law would fill her mouth with water and then suck the baby’s soft spot out. *DO NOT TRY THIS AT HOME!!*
Sunken in soft spots can be a sign of dehydration because there is lots of blood vessels in that area.
The bones in your face and head have cavities and tunnels (called sinuses) that allow nerves and blood vessels to travel through, as well as keep air pressure stable.
Questions
Question 1: Skull fracture? Can possibly happen on a suture where two bones separate, but more often an actual crack in one bone.
Question 2: Is brain bleeding always dangerous? Always potentially fatal? Yes, because your brain is closed in. Brain bleeds are classified into levels, and part of it has to do with how deep in the brain it happens, and how much pressure it puts on the things around it. Blood vessels are found all throughout your brain, and the blood that flows through them has its designated space. If the blood comes out of the blood vessels, then it starts crowding out the things around it (which can be important parts of your brain). Sometimes people may have a brain bleed and they will remove part of the skull bone to relieve the pressure.
Another Story
Orbital hemorrhage caused vision loss and feeling loss in lower extremities. If the nerve signal is interrupted temporarily, then the functions of those parts will return. If the nerves are damaged permanently, then those functions will be lost permanently. This was caused by blunt force trauma. As long as the rest of you is healthy, and the injury is fully healed, I would not expect it to happen again out of the blue.
Party Trick
Where does the bottom of your brain sit? Your cranium has a floor. One of the bones that make up the floor is called the Sphenoid bone (my favorite bone).
You can reach it and wiggle it and help with sinus pressure and drainage (it’s a neat trick!) It works by creating tiny pressure differences in your sinuses.
The outside of your skull bones are rather smooth. The inside of those bones are bumpy and jagged because it gives places for the membranes to anchor and keep the brain buoyant and centered.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credit: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Skin Cancer ABCDE [Show Notes]

Review
Epidermis = top layer of skin. Living cells divide and then add in proteins that causes cells to harden as they die and become and protective layer to keep out water and dirt and critters. Some of those proteins give your skin its color (melanin) and they help block and reflect UV light from the sun to keep the living cells from being damaged.
Mutations = if UV light damages the cells’ DNA, then when the cells divide and replicate, they copy the “error” and reproduce an abnormal cell. If certain mutations cause the cells to die, others cause the cells to be weak, but others cause the cells to become cancer.
3 types of skin cancer
- Basal cell carcinoma – most common of these 3, more common in people with fair skin. Skin growth is flesh colored, can look like skin tags. Caused when a basal cell gets mutated and starts to grow.
Squamous cell carcinoma – more common in people with fair skin. Scaly patches or sores that open, start to heal but reopen and never heal. Caused when a keratinocyte (living, dividing skin cell) gets mutated in the middle of replicating.
Melanoma – Moles are just a place where a lot of melanocytes gather in one place, but sudden moles or dark spots can be the tip of a bad iceberg. This is the deadliest type of skin cancer. Caused by mutations in the melanocytes.
Some benign (harmless) skin characteristics can resemble skin cancer, thus it’s easy to overlook them in the early stages.
A tool for early detection of melanoma
A – Asymmetry – you can’t fold it in half and all the edges match
B – Boarder – jaggedy, sharp boarders
C – Color – uneven color
D – Diameter – > 6mm (bigger than the eraser of a #2 pencil)
E – Evolving – changes shape, size, or color in a short amount of time (< 1 month)
This is why the National Skin Cancer Foundation recommends you do a monthly skin scan to check skin characteristics for changes or new ones.
Early detection is the number one step to improve survival of all cancers.
Precancer = Actinic Keratosis – dry and flakey places in the skin, can be the precursor of Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Usually shows up after 40 years old.
Cancer is not just a disease that happens to the aged, but as you age, the probability of you being exposed to something that could mutate your cells goes up.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Skin Conditions [Show Notes]

Dry skin
It is usually due to your skin not having enough of its own natural oils (probably strips from soaps, cleansers, chemicals). Moisturizing lotions and creams are “greasy” to try and match the oil of your skin. The oil make the skin waterproof – keeps water out, but also keeps water in (prevents evaporation)
Eczema – dry skin with an immune/inflammation component. The deeper layers of the skin will release inflammation chemicals that irritate the other cells in the area and lead to redness, pain, and swelling. It’s common for kids to have eczema but then grow out of it, but other conditions can cause eczema to flare (in my case, pregnancy).
Rash
Rash is one of the most ambiguous symptoms to try and figure out what the root cause is. Rashes can be round or splotchy, symmetrical or asymmetrical, raised or flat, big or small. Rashes are caused by some type of inflammation process (most commonly histamines). Rashes are a sign that your body has been offended by something – either from the inside and then the chemicals reach the skin to cause rash, or from the outside that touched your skin and caused chemicals to be released.
*Hives – a very distinctive rash with raised, irregular borders that may be red, but can also maintain their “flesh color”. Most commonly involve histamines, thus antihistamines (like benadryl can help them go away). Can possibly be triggered by stress (the stress hormones cause a chain reaction of chemical release which may lead to hives).
*Viral exanthem – “exit rash”; a rash that kids will get when their body has finally beat a virus. Some start at the top of the body and then moves down to their feet. Others start on the torso or core and then move out to the extremities. Antihistamines do not help it, but they rarely hurt or itch or bother the kid in any way.
Acne
There are different pores in your skin (sweat glands, oil glands, hair follicles). The oil on your face helps to trap bacteria and dirt that could get deeper in your skin and possibly hurt you. The goal of cleaning your face, is to cleanse off the “dirty” oil, but not all the oil (because the result is either dry skin or over-production). So the dirty oil plus the shedding dead skin cells can clog up any of these pores. Blackheads are specifically when hair follicles are clogged – and they look black b/c the melanin proteins that get built into hair can be seen. Generally small blackheads and whiteheads are not painful, unless a lot of bacteria are involved and they begin to fester.
Cystic acne is when a larger area that involves multiple pore or hair follicles get clogged and infected with bacteria and then the spot can become swollen and painful (and unsightly).
Hormones regulate the oil production, that’s why puberty increases acne, stress increases acne, all of the transitions surrounding pregnancy can increase acne. As long as you have hormones, you’re going to have a risk of acne. Also, working in really dirty environments can increase the amount of dirt that could clog up pores.
Infections
Ringworm = tinea corporis (there’s no worm involved, it’s a fungus). Classic circular rash that is red and flakey and possibly flesh-colored in the middle.
If it’s on your head (tinea capitis = cradle cap). If it’s in your groin (tinea cruris = jock itch). If it’s on your feet (tinea pedis = athlete’s foot).
Tinea vesicolor = the fungus causes the skin to lose pigment (this is NOT vitiligo, which is the death of melanocytes and they don’t grow back, Michael Jackson).
Candida is the yeast that is a part of your natural skin flora, but can lead to rash if it gets out of balance.
Bottom Line
If there is anything on your skin that bothers you, see your doctor!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
How Sunscreen Works [Show Notes]

Two products to protect your skin from sun exposure
- Sunscreen – filters the sunlight *like a screen on a window*; made up of organic compounds (like chemistry, not vegetables) that absorb UVA and/or UVB rays that reach your skin. These are the products labeled with SPF numbers.
- Sunblock – used to be opaque because it is supposed to completely block any sunlight from getting to your skin. *Think Screech from Saved By The Bell*. Full of reflective particles to bounce the sunlight away from your body. The particles have been micronized by technology so it is transparent to your eyes, but not to the UV light from the sun.
Lesson on Light
The light comes from the sun. There’s visible light (ROYGBV) and that light bounces off of things and as it goes in your eyes, that’s how you can see things. Along with the light we see, there is ultraviolet light (waves of light that are shorter and more energetic that the violet color light). There are 3 types of UV light – 1 is absorbed and reflected by the atmosphere so it never makes it to us. Then there is UVA and UVB. UVA is more energetic and is most responsible for causing cell mutations that lead to cancer. UVB is less energetic and is most responsible for causing your skin to tan.
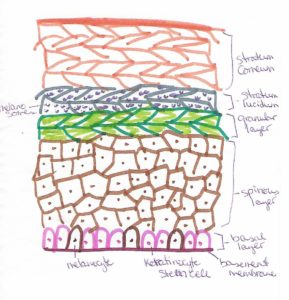
UV rays travel through these layers of the skin and stimulate the living and dividing cells to divide more and create more melanin. Reminder: melanin is your skin’s natural skin protectant because it will absorb UV rays in the higher layers to help prevent it from reaching the dividing cells.
SPF Math (Sun Protection Factor)
Step 1: find out how long you can be out in the sun without protection before your skin starts turning red or burning (example: 15 minutes)
Step 2: Multiply that “unprotected time” by the SPF number on the bottle (SPF 15) to get your “protected time” (15 x 15 = 225 minutes = 3 hr 45 min**)
**This is only if you don’t sweat and don’t get wet. But it’s very hard to be in the sun and NOT sweat. Plus your natural skin oils dilute it the longer it stays on the skin.
Protect Yo’self
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends reapplying sunscreen every 2 hours no matter what. They also recommend that you use SPF 15 (or higher) sunscreen. It should block UVA and UVB. Use it every day, especially on your face, and use it all year round. The daily UV exposure, if you’re unprotected, is what they suspect leads to a greater chance of skin cancer.
They also recommend UV-blocking sunglasses.
Clothes and hats are the best way to protect your skin from sun exposure.
Stay inside during peak hours (10 am – 4 pm) of radiation (less atmosphere to block and deflect sunlight).
Do a monthly, head-to-toe, skin scan to check for new or changing moles, freckles, and skin tags (or get a friend to help). EARLY DETECTION!!
Have your doctor check your skin once a year.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Vitamin D [Show Notes]

Vitamin D Basics
Vitamin D is made by your skin.
Lots of foods are fortified with Vit D.
Vitamin D2 is plant-based. Plants make vitamin D then you eat them and absorb it. This is also the type of Vitamin D that is added to other foods.
Vitamin D3 is animal-based. You absorb very little Vitamin D from animal food sources. This is the type that your skin makes.
Review
The membranes of your cells are made up of cholesterol. It allows them to stay fluid and flexible, and it allows diffusion of some nutrients.
UV-B rays come down from the sun and travel through the top layer of your skin. Those rays interact with the cholesterol in the skin cells and cause it to break away and it starts a changing process as that loose molecule makes it way to the bloodstream. *Think the Hulk transformation*. By the time it reaches the bloodstream, it has become D3 (~ 12 hour long process).
Vit D3 = Calcitriol (tri = 3)
Vit D2 = Calcidiol (di = 2)
The news will tell you that Vit D is needed to prevent the Winter Blues or that it’s good for your bones.
Deeper Stuff
Vitamin D has 2 jobs to help with your bone health. It tells your intestines to make calcium-carrying and phosphorus-carrying proteins, so when you eat foods that contain calcium or phosphorus, the cells of the small intestines will have the ability to transport these molecules into the bloodstream. Then in your periosteum (the membrane that covers your bones), Vitamin D works with parathyroid hormone to tell the periosteum cells to make the same kinds of proteins to get the calcium out of the blood and into the bone-building process.
Vitamin D also has an important role in your immune system. It plays a part in cell differentiation. It helps an immune system cell know which type of cell it needs to specialize as (B-cell, T-cell, macrophage) to do the optimum job based on the type of invader that has entered your body.
While sun exposure stimulates Vit D production, there has to be a balance to avoid skin aging and risks of cancer. Taking Vit D supplements can be a safer alternative.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Skin 101 [Show Notes]

Skin 101
Your skin is the largest organ of your body.
It has 3 jobs: Protection, Regulation, Sensation
Natural complexions are being viewed as more beautiful than a “tan”.
3 Layers
- Epidermis (above skin) – waterproof, gives you your color, the layer we see
- Dermis-Epidermis junction – a protein layer containing collagen and elastin to give skin flexibility and stretchability
- Dermis – where your glands, hair follicles, and nerves are
- Hypodermis – (below skin) – houses adipose tissue for insulation, and blood vessels
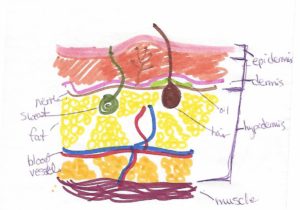
The Epidermis is made up of several separate layers based on what is happening in the cell’s lifetime.

The basement membrane sits right on top of the Dermis-Epidermis junction, made up of fibrous proteins to be a solid foundation.
Epidermis Layers
- Basal Layer – Keratinocytes (makes Keratin) and Melanocytes (makes Melanin) – stem cells.
- Spinous Layer – Cells are actively dividing and getting squished together
- Granular Layer – Cells start making the proteins (keratin or melanin) that they are coded to make and it fills up all the intracellular space; the organelles of the cells get crowded out
- Lucid Layer (Clear) – Keratinized cells are clear; Melanin-filled cells are colored. Cells are officially dead. Cells become coated in a hydrophobic (afraid of water) oil.
- Hard Layer – cells are tightly packed together and dry; the layer we can touch.
These cells are being continuously produced and shed off and replenished because the skin takes a lot of abuse.
Deeper Stuff
UV light from sun or tanning beds (heaven forbid!) stimulates melanocytes to divide faster and create more melanin (because melanin is reflective and keeps UV rays away from the important cells). This is how a tan is created. But during times of huge exposure, like tanning beds, there’s not enough melanin to keep all the UV rays out so those rays can wreak havoc on the collagen and elastin proteins. This is why over-tanned skin ages faster.
Hydrating makes sure that the living and dividing cells are plump and as healthy as possible so when they move to the next layer, they are well nourished.
Protection: keeps dirt and bacteria out; protections from UV radiation
Regulation: releases sweat to cool the body’s temp; subtly moves blood vessel closer or farther away from the surface to either cool the warm blood (like after exercise) or keep it warm (like in the winter).
Sensations: allows you to feel things that touch you or come close to you.
I can’t seem to find any free footage of the original episode (Season 1, Episode 3) without having to sign up for a free streaming service. The Mythbusters did a “revisit” of their Goldfinger episode. Netflix the original, if you can.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Hair Problems [Show Notes]

Alopecia – hair falls out in the same area all at one time. Kind of like crop circles.
3 Stages of the Hair Follicle life cycle
– Anagen phase – active phase, cells are multiplying, hair is growing
– Catagen phase – resting phase, “cat nap”
– Telogen phase – shedding phase
Hair thickness is determined by 2 things: the density of hair follicles (how many follicles in one area) and how large a single hair follicle is (thick vs fine hair).
male patterned baldness – receding hairline from front to back, and the loss of the hair on the crown of the head.
Female patterned baldness – the overall thinning of the hair.
Hirsutism – females get male-patterned balding due to testosterone imbalance
Why does all your hair fall out after you have a baby??
Telogen effluvium – a mass exodus of hair follicles
This can also happen when the body goes through extreme shock or trauma.
There is a condition called post-partum alopecia – this is temporary, and hair grows back afterwards.
Itchy Scalp
Dandruff is caused by the inflammation of the scalp. Inflammation causes skin to be dry and itchy. The topmost skin layer releases in larger amounts, thus the pieces are visible, opposed to when the skin naturally sheds, it’s microscopic so you don’t usually see the dead skin cells you lose.
Tinea capitis – ringworm on your scalp, aka cradle cap. Usually requires an antifungal to get rid of it.
Tidbits
Hair can actively grow for up to 6 years.
Since hair is dead cells, hair hangs onto the DNA and it can be used to identify people (missing persons) or for paternity tests (who’s your daddy)?
Dying and perming affect the proteins that give it color or keep it connected.
If someone has had prolonged exposure to toxin (carbon monoxide, heavy metals, smoking), the hair shows markers of that damage from the toxins. It can also hang on to markers from being exposed to illicit drugs. It’s like a timeline of what you’ve been exposed to.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Hair Vitamins [Show Notes]

Disclaimer
If you live in a modernized country, the food that you eat will give you more than enough of the vitamins you need, because you have access to a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, plus tons of food products are fortified with vitamins. So rarely is someone deficient in a whole bunch of vitamins all at once.
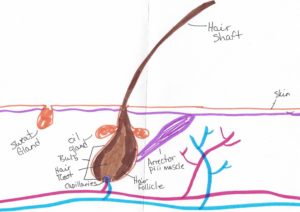
Vitamins
- Biotin (Vitamin H – antiquated; Vitamin B-7) – a cofactor that works with your enzymes to help transport carbon dioxide – which is a waste product in your body. Carbon dioxide is created in fatty acid production, amino acid metabolism, and gluconeogenesis (making glucose out of things that aren’t glucose). Peanuts is a huge source of biotin. Your natural gut flora make biotin for you!! So apparently good for your whole body, not just your hair.
- Vitamin C – responsible for helping collagen production. Most directly related to hair, skin, and nails. Collagen allows cells to be stretchy and elastic and more flexible against abuse. It also helps your digestive tract absorb iron (callback!).
- Vitamin E – is an oil-based vitamin and an antioxidant. Lots of health fads scream at you about free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that are waste products from different processes that end up with a non-neutral charge (so either positive charge or negative charge). So if you remember chemistry, they prefer to be neutral, so free radicals want to steal charges to neutralize, and can sometimes steal it from your DNA and lead to major cell damage. An antioxidant is a molecule that finds an oxidized free radical and donates a charge so that it’s neutral again (and the antioxidant is able to cope better with losing an electron or two without becoming radical itself). Vitamin E focuses on the free radicals from fatty acid processes. Again, good for your whole body, not just your hair.
Supplements
- Omega-3-Fatty acid – an oil, a fatty acid chain that goes into the production of your skin’s natural moisture. Your skin needs its natural oil to trap up dirt and bacteria, as well as keeping the moisture from deeper inside your body from evaporating out. So each hair follicle has an oil gland with it to keep the hair moisturized. The new information about the importance of your hair’s natural oil has encouraged the “no ‘poo” movement. This is more directly related to your hair, but a lot of other places in your body benefit from O3FA’s.
- Iron – responsible for helping your red blood cells to carry around oxygen. This is most likely the only nutrient in this list that someone would need to truly supplement, mainly because iron deficiency can be caused by several things, some of which are genetic. People with prolonged anemia have dull hair, skin, and nails. Again, good for your whole body.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Hair 101 [Show Notes]

Key Words
- Keratin = a fibrous protein that cells make when they are about to die.
- Cornification = the process of a cell filling up with Keratin and becoming hard.
- Follicle = the hole in the skin where the hair grows out
- Melanin = a protein that adds color to cells of the body (most familiar because they help skin tan)

Hair Basics
Arrector pili = the muscle that makes your hairs stand up
Fingernails and hair are made out of keratinized cells. Nails are harder to protect the more tender skin below (and are a primitive tool). Hair is tightly stacked but more flexible. They are both dead cells so they don’t absorb nutrients or feel.
Because hair grows when cells lining the follicles fill up with keratin and die, it grows from your scalp, rather than being added to the ends.
Cells in the bulb divide every 23-72 hours.
Straight or curly is determined by the shape of the follicle. Symmetrical = straight, asymmetrical = curly. Square follicles is a myth.
There are 2 types of melanin – eumelanin = dark colors; pheomelanin = light. Genetics determines what ratio of each type your skin produces thus determines the color of your hair. It turns gray because the cells are absent of all melanin types.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Episode 51 – Behind the Scenes

Stuff Happens!
Katch.me shut down – I panicked!
We bought a new house.
So we moved into the new house.
Then, we went on vacation.
And finally, we sold the old house.
Celebrate!
I had my 1 year anniversary on Periscope. (My first Periscope broadcast was about being nice to people who work on holidays, because they didn’t get the day off like you did!)
Pharmacist Answers Podcast will be ONE on July 17th!
New episodes will begin July 6th.
Keep an eye out for me on Facebook live.
Come see me on Periscope 9:02 am Eastern on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays.
@CynHendrix or periscope.tv/cynhendrix
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Collaboration in Your Health [Show Notes]

Collaboration is a hot topic in many arenas these days, but healthcare seems to still struggle with it.
Holla!
My friend, Ronei Harden, has a periscope show called Coffee Talk. Recently, she has talked a lot about collaboration. You can watch her live or see some of her older conversations on her YouTube channel.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
If Healthcare Cared [Show Notes]

Holla!
If you’re a fan or follower of Jon Acuff, you will have heard of 30 Days of Hustle. Started as a set of emails and a Facebook group, but has become a way of life for many. It may be too late to join in on Jon’s #30DOH community, but it’s never too late to start hustling! (And I’m not representing Jon or 30DOH, just a fan…because with them, this podcast wouldn’t be here!)
Not a lot of information today, but here’s the take-home message…
Treat those you encounter in the healthcare arena with respect, and confidently and respectfully demand they do they same.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Insurance Cards [Show Notes]

Using Your insurance Cards
- Know your cards
Different companies print and send their cards differently, so you need to be familiar with yours.- Medical card: if it doesn’t say “Major Medical” or “Health Plan”, look for clues like copay structure (UC $10/Spec $25/ER $75) to indicate what copay you will pay at which type of healthcare business.
- Dental card: should say “Dental”, nothing else special about it.
- Prescription card: Some prescription insurance companies have names with “Rx” in it, which is the abbreviation for prescription or pharmacy. Other times, there will be numbers or codes that are labeled “Rx Bin” or “Rx Group”. Sometimes this info will be in a little box on the side of the Medical card.
- Don’t let logos lie to you
- Sometimes insurance companies are managed by an umbrella company that may also own a large retail chain pharmacy. They will put their logo on the card in big, bright print. This does not always mean that is the only place you can go for prescriptions. Don’t let it fool you!
Kaiser Permanente can be a great healthcare solution for some people, but not every company is for every person. They have their own extra set of rules. So, if this is your insurance company, make sure you know their rules, so you don’t get stuck without care or with paying a lot of money for care.
Following these two steps can ensure that you do not have interrupted to delayed care, and that you hang on to your power to choose where you get care!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Insurance Speak [Show Notes]

Coverage Terminology
- Formulary – a list of medications that insurance decides they will pay for. They can change this whenever they feel like it.
- Prior Authorization – insurance requires the payment of a particular medication or service to be authorized prior to them paying for it and/or you receiving it. Usually require documentation and justification from your doctor.
- Networks – Providers in the Network usually have a negotiated discount or other beneficial contract with the insurance, which will translate to lower costs for you.
Payment Terminology
- Premium – paying dues to be in the club. And being in the club means that the insurance company will have to pay for your care if you get sick or hurt.
- Deductible – a portion of costs that you are 100% responsible for before the insurance company chips in. Low premium = high deductible.
- Copay – Co = together, pay = payments. You and your insurance are paying the total bill together. Copays are usually standardized, and are a price predetermined by the insurance company. Medication copays are broken down into Tiers.
- Coinsurance – rather than a set price, it’s a set percentage. Based on the total cost of the service, the price you pay may change.
- Out Of Pocket (OOP) – some companies keep track of all the money you pay and they have a limit (called Lifetime Maximum or Lifetime Limit). If your costs reach that limit, the insurance company will take care of everything after that.
Your Money
- Health Savings Account (HSA) – YOUR money that you put back to use to pay for healthcare costs in the future. This money will roll over.
- Health Reimbursement Account (HRA) – an incentive from your employer or insurance for you do things to prevent illness, and then THEY will give you money to pay for your healthcare costs. This money will roll over as well.
- Flex Spending Account (FSA)- YOUR money that you put into an account to pay for healthcare costs or health related items (some OTC things are approved). They usually require receipt submission to prove you purchased approved items. But if that money is not used by the deadline, it does NOT roll over, you do not get it back.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Probiotics [Show Notes]

Good for Your Gut
Probiotics are advertised for digestive health, but they are good for your whole body.
Normal flora = bacteria and yeast in a nice, happy balance. This comes partly from when you exit your mother’s body, others come from your environment.
Any probiotic is better than none at all.
Probiotics – good for all your body parts!
WARNING!
If you eat yogurt, watch for sugar content!
Eat unpasteurized dairy at your own risk!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
It’s All About Sleep

Gotta Breath While You Sleep
Apnea = stopped breathing
When you metabolize the fat stores when you’re losing weight, the main by-product of that process is carbon dioxide. You breathe away your fat!!
Getting better sleep can be the trick to untangling the knot of many health problems.
Medication can make apnea worse. So can other things too.
Caffeine helps you stay awake (read and listen here). Sunlight does much more for you in helping you wake up (as little as 15 minutes of sunlight a day).
Light Makes a Difference
Sun comes up –> serotonin –> happy, awake, productive
Sun goes down –> melatonin replaces serotonin –> sleep
People who work third shift have to use a lot of tricks for making daytime to feel like night so you can sleep.
Can’t just supplement serotonin because a lot of biologicals don’t survive the digestive and absorption process to get used by the body.
Electronic curfews are a good idea.
Light that helps us see is actually a combination of different colors of light (based on their wavelength). The blue wavelength of light is what stimulates our eyes. So, if you have to do work at night, blocking that stimulating light can help you sleep once work is over.
Working third-shift is now considered a carcinogen.
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) runs while you’re sleeping.
*Links in this post are affiliate links*
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Doctors Get Sick Too [Show Notes]
Healthcare Professionals Get Sick Too
The healthcare professionals that take care of you are human too!
Yes, they are in a job to serve, but they’re not immune to germs or stress or hunger.
Please treat the people that serve you like humans!
That is all!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Disagreement with your Doctor [Show Notes]

Disagreements happen
Be an adult about it.
You can respectfully let your doctor know you’ve been trying to learn things on your own. Do not say “I learned it on Google. Provide your doctor with the information from a respectable resource.
It’s not about getting the doctor to do it your way, but about everyone gaining knowledge, being respectful, and doing what’s best for YOU.
The goal is to build the best healthcare team for YOU
If the disagreement is strong on the doctor’s part and they show (or say) they don’t want you empowered and participating in the decision-making about your treatment and health, you may need to re-evaluate.
If you find yourself having to choose a new doctor, you can take an opportunity to interview the doctor. Ask the hard questions.
Insurances and doctors try to imply that you don’t have a choice about the doctors you see, but don’t be fooled. You still have the power to choose.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Caffeine and Headaches [Show Notes]

How Blood Flows
Blood vessels are like flexible pipes that run to every nook and cranny of your body. When they dilate (or widen), they let more blood through; when they constrict (or narrow), they let less blood through. If the blood vessels constrict and the body part at the end of that path feels deprived, it may send a pain signal to the brain.
If the blood vessels constrict or dilate quickly, your body will feel it and it may be translated as pain.
Headaches can be the result of an overall constriction of blood vessels in the head.
Your brain is full of neurons (nerve cells), and even though they translate pain, they don’t sense pain.
Caffeine Can Help
Caffeine can gently open up constricted blood vessels.
Your body is efficient, so when you sleep, certain blood vessels to certain parts of your body (like digestive tract and skeletal muscles) constrict to maximize blood flow to other places. Once you wake up, the process by which the body re-dilates those vessels can be slow. Exercise can make it faster. So can caffeine.
The reason why caffeine helps us wake up: it dilates the blood vessels so more blood flows to the areas of the brain that control attention and focus and alertness.
Caffeine pill = 200 mg
Water for a headache?
If you’re dehydrated, your blood will be slightly thicker and may be harder to get to the nooks and crannies, and that can cause headache. Dehydration can also cause low blood pressure can lead to headache.
The reason caffeine is in OTC headache pills – 1) caffeine can dilate blood vessels, and 2) it speeds up heart rate with increases how fast the other meds flow through the body.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Cholesterol Basics [Show Notes]

Fat Basics
Fats don’t mix with water. Some fats are liquid at room temperature (oils), some fats are solid at room temperature.
Because so much of your body is made up of water, fats are very unhappy there. So your body will take this “head” that likes water, and sticks it on the lipid “tails”.
*Correction: This combination is called a Phospholipid
Then they will form a little ball where all the water-hating tails are inside, and all the water-liking heads are on the outside. This is called a Lipoprotein.
Cholesterol
LDL = Low-density lipoprotein (“Bad”) HDL = High-density lipoprotein (“Good”)
Density = the amount of stuff you can cram in a limited space
– A lot of stuff in a small space = high density
– A little bit of stuff in a big space = low density
In the lipoproteins, extra proteins are added to help direct it where to go. HDLs have more proteins to help them stay focused than LDLs, so LDLs are like distracted drivers…
The Egg Controversy (while I avoid a lot of HuffPost articles, and I don’t know much else about this author, I agree with 90% of what he says here – and that’s more than I can say about other information I find out there)
LDLs also have more triglycerides crammed into them. Triglycerides have 3 water-hating tails instead of one.
What’s the magic number?
You don’t need your cholesterol number to be zero. You need cholesterols to build cell membranes and hormones, you just don’t want there to be too much of it.
So the LDLs are less directed so they end up crashing into each other and sticking together. Then if they crash into the artery wall, they may get stuck there and just becomes a place where more stuff can get stuck. This is how atherosclerosis and blockages happens. A bunch of cholesterol is stuck to the walls of the arteries.
There is NO magic number!
HDL: > 40 men, > 50 women
LDL: < 100
Trigs: < 150
TC: < 200
The Bottom Line
HDLs and LDLs are the types of packages your body uses to carry fatty acids around your body.
The main hub of all this cholesterol packing and shipping and using is your liver. Once the liver is done using all the fatty acids it needs, if there’s a bunch extra, it starts packing them away into adipose (or fat) tissue and storing it wherever it can around your body. And there is NO LIMIT to the size of the fat stores!
The Statin Controversy (this is a great summary – the bottom line being that the people recommending “statins for everyone” stand to benefit greatly in their pocketbook if more people in the world actually started taking (aka buying) statins.
Familial Hypercholesterolemia = genetically inherited high cholesterol
Lifestyle changes (eating healthy foods and an appropriate amount of exercise) can never be bad for you!
If you take your coffee the “bulletproof” way, consult your doctor first.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
I Think You’re Smart [Show Notes]

I think you’re smart
You’re smart, I know you are! I want you to apply those smarts and help me out a bit.
Piles of information thrown at us about our health, some new treatment or medicine, or some new aspect of a disease. The media is flat out MEAN about how and when it presents this information. Usually, it’s incomplete, biased, and twisted into a scare tactic.
Anyone with a brain will know that anything in excess can be bad.
Some tips on judging the source of information
- Are they trustworthy? Have you even heard of them or their site?
- What is their reputation of presenting “shock and awe” headlines just to get views, clicks, or attention?
- Is it a celebrity or politician who wants some screen time and just wants to be the loudest voice in the room?
Critical thinking is a dying skill, please don’t let it go extinct.
Consider the Source
Science and medical information is classified based on how close to the “horse’s mouth” it is. Scientists who do the study, write the reports and articles, and publish it in journals themselves – those are called primary sources. To be trustworthy, they have to state any limitations their study had, confounding factors, and any biases (aka money paid by someone who cares, like drug companies or lobbying groups). Then there may be a group of scientists or statisticians that take several primary resources that studied the same thing and compare all their outcomes and come up with an overarching conclusion – those are called secondary sources. Articles that reach the public and may have citations of using primary or secondary sources for some of the information presented are called tertiary sources. They are so far removed from the primary source that they CANNOT be used for academic research!
Again, critical thinking skills are vital for our success in society. Don’t follow the fads! Don’t allow yourself to be duped by people who line their pockets with money from people who are ignorant about the subject they’re screaming.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
5 Things Your Pharmacist Is Not [Show Notes]

5 Things Your Pharmacist is Not
- A mind-reader (neither is anyone else)
- A robot (as is anyone else who serves you)
- A prescriber or diagnoser
- “Besties” with all the doctors in town
- Your personal assistant or secretary
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
DIY Diaper Cream [Show Notes]

Diarrhea is not fun, diarrhea in kids is not fun, diarrhea in kids in diapers is certainly not fun. Diaper rash can flair in just one or two diaper changes.
Diaper rash products
- Protectant ointments: like vaseline, kind of greasy but provide a moisture barrier to keep the skin’s moisture levels from getting out of balance.
- Zinc Oxide: like Desitin, white or opaque and thick, keeps the moisture in the skin in, and the moisture outside the skin out. More completely covers diaper rash so really sore spots can heal faster.
Diaper Rash
Some diaper rashes are caused by a yeast imbalance, so doctors may recommend an OTC or prescription yeast cream.
Sometimes diaper rashes can be really itchy (even though little babies can’t tell you they itch, so all they do is cry), so OTC or prescription steroid creams can be used.
Diaper rash from diarrhea is usually caused by acid that is released in the liquid stool. For babies in diapers, when acidic diarrhea exits the body, it hurts; but then it sits in the diaper and continues to hurt and irritate the skin. Not to mention the irritation that may have already occurred due to frequent diaper changes.
A frequently recommended fix for diaper rash is air. Letting the rash air dry and not be closed up in a diaper can work a lot of times. That doesn’t sound like a great solution if baby has diarrhea.
There’s a butt paste that pharmacies can compound with a doctor’s prescription.
Recipe
- Aquaphor ointment (OTC) – kind protectant
- Mylanta (OTC) – antacid to neutralize acid
- Cholestyramine powder (Rx) – medication that treats cholesterol by trapping up lipids in the intestines so the body doesn’t absorb it – it can trap up bile that comes out in the stool
You can use 2 out of the 3 ingredients and do this yourself with a couple tools in your kitchen!
- Heat the tub of aquaphor on a hot plate, or warm it in a double boiler, until melted. (You don’t want to have to remove all the ointment from the tub to melt b/c you’ll waste some and it’ll be really gooey).
- Add 2 Tbsp (30 ml, 1 fl. oz) of Mylanta to liquid Aquaphor and stir well.
- Let it cool! Do not put warm ointment on your baby!
- Apply to baby bum as needed for diaper rash.
Doesn’t have to be just for babies….
Anyone who has had diarrhea and experienced the burn from the acid and irritation from frequent stools can benefit from this product.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
2 Ways to Help Your Pharmacist [Show Notes]

2 things you can do to help your pharmacist help you better
- Have patience. The pharmacist is one person, and they have one mouth and one set of ears, and can only listen and talk to one person at a time. You want undivided attention, and we want to give you undivided attention, and to get that, there may be a short wait.
- Be honest. Full disclosure is important when it comes to your health conditions, allergies or intolerances, and questions or concerns about anything related to your health. Pharmacists in most states have a legal responsibility to counsel or offer counseling to patients in certain situations, but they can’t read your mind.
Sorry for the soapbox! (Well, maybe I’m not!)
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
3 Ways People Get it [Show Notes]

Three characteristics of people who take charge of their health
- Stop placing blame. It’s not my fault electronics malfunction, and it’s not my fault the nurse hasn’t returned a phone call.
- Get the whole story. They find out what I’ve done, they find out what the doctor’s office staff has done, they find out what their insurance has done… because there’s more than 2 sides to a story.
- Take decisive action. If they learn something new about their situation based on the 2 things above, they take action to make progress towards getting problems solved.
The big picture
They take responsibility for their own health. If there are steps you can take on your own to get the outcome you desire, take them. If someone on your team isn’t meeting expectations or doing their part on your team, you get to choose: do you talk to them and get on the same page, or do you choose someone else to be on your team.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Reflux vs Ulcer [Show Notes]

Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disorder
GERD, or just Reflux.
Reflux is a word that is used to describe something in your body that flows backwards. The fluids in your body have a certain direction they naturally flow for your body to work properly. If they start flowing backwards, it’s called reflux, and can lead to problems.
Is that like heartburn?
Yes, heartburn is a type of mild reflux. Something (like a certain type of food or overeating) causes the stomach acid to bubble back up into the esophagus.
Overeating or other physiological disorder can cause the lower sphincter to not close tightly or completely.
Ulcer
They lining of your stomach produces the acid, thus it’s intended to be resistant against the acid. The lining of the esophagus is not intended to handle that acid. And stomach acid is way more acidic that our saliva or acidic foods that we may eat.
Now, if the acid-producing (and acid-resistant) lining of the stomach wall gets injured, and the layers underneath come in contact with the acid, it causes pain.
Would that cause someone to throw up blood?
Yes, it possibly would. Any tissue that is living and working in your body, requires a blood supply to bring in nutrients and carry out waste. So, the walls of your stomach is full of blood vessels. If the acid, eats through the layers and gets to the blood vessels, that blood will spill into the stomach. Unfortunately, your digestive system isn’t intended to digest large amounts of blood. The pain from the acid plus the large amounts of blood can lead to nausea and vomiting.
How I assess ulcer or reflux
Where does it hurt?
– Reflux: in the esophagus or throat (even to the point of hoarseness)
– Ulcer: Stomach
Does it hurt worse when you’re hungry or after you eat?
– Reflux: hurts after food has gone into stomach or you lay down at night because you don’t have gravity holding the acid down into the stomach.
– Ulcer: hurts when the stomach is empty because the acid only comes in contact with the stomach lining, rather than having food to work on.
Treatment
The treatment for both is the same. The goal for both is to reduce the acid production. People will try to self-treat by taking tons and tons of OTC antacids (liquid or tablets). Antacids are bases, so they goal is to neutralize the acids, but once that amount has moved into the intestines, the base is gone and the acid is till there. Other acid reduces are OTC as well. Histamine 2 Receptor Blockers (Pepcid, Zantac) can start to work within 30 minutes. Proton Pump Inhibitors (Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium) can take up to 2 weeks to reduce the acid, so not intended for instant treatment.
Bottom Line
Whether it’s ulcers or reflux, your doctor needs to know what’s going on so they can monitor your progress. Anything that manipulates cells in your body (whether stomach cells damaged in an ulcer or esophageal cells being corroded by acid) can cause cellular changes that may become cancer.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Lice [Show Notes]

Myth #1: Having lice means that you’re dirty
Truth: Lice like clean hair. When you shampoo, the soap strips your hair of its natural oil. So while you think your hair is clean, it is also very grippy. Thus, lice can hang on better to move around.
Solution: Don’t wash your hair – ha! At least allow your natural oils to stay in your hair, or use a leave in conditioner or other product that makes the hair “slippery”.
Will dry shampoo attract lice if you’re not washing your hair?
Dry shampoo works like baby powder – it absorbs the excess oil and moisture, but doesn’t dry out the roots of your hair as soapy, foamy shampoos.
Jump on the no ‘poo bandwagon!
Myth #2: Live for a long time off your hair
Truth: Lice require a warm place and a blood supply for survival. They like to hang out at the base of the head and neck and around your ears. They may fall off on couches backpacks, and car seats, but they rarely survive there long enough to transfer to someone else. It is mostly spread by head to head contact (sharing a bed, sharing a hairbrush).
Myth #3: Pets can carry lice
Truth: They are only spread human to human. Other parasites that like humans (i.e. mosquitos, fleas, ticks) can be spread by pets, but lice cannot.
What to do?
The overuse of over the counter pesticide products that kill lice is encouraging them to build up resistance. Critters, large and small, will change and mutate to ensure their survival. This is why the news talked about them as “super lice”.
Good news: They’re not resistant to vinegar. Diluted vinegar is not harsh on your hair and doesn’t strip oils, but it can dissolve the glue that hold the eggs, or nits, onto the hair shaft. This will allow the eggs to wash out or be combed out easily.
Tea tree oil is intended to suffocate them or repel them completely. No proof that it’s really effective, but it can be mixed with the vinegar to help your hair smell better.
Some of the standard chemical products can be very strong and not intended to be used on children under a certain age. Some of the chemicals work by disrupting the parasite’s DNA and neural system, humans are just way bigger than lice so it would take way more to hurt humans, but the risk is there.
Lice furniture spray – intended to be used on furniture that has long exposure (4+ hours) with the infected person.
If there are positive signs of lice, it may take more than one round of treatment and combing to get any new ones that hatch.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Don’t Share Your Cold [Show Notes]

Cold Virus
Rhinovirus. Rhino = nose. The cold virus accesses the body through the nose and mouth, and it uses the cells in the sinuses and throat to replicate.
Viruses require a host cell to replicate, therefore they don’t live very long outside of a host. The cold virus can live on a surface for about 3 hours.
During the initial infection and multiplication stages (first 3 days), you are the most contagious even though you have no symptoms of being sick.
Cold symptoms
- Runny Nose
- Scratchy throat
- Cough
- Sinus congestion
- Tiredness
- Mild fever
- Possible body aches
“Morning sniffles” not a cold.
Your tonsils are a major hub of your immune system. So, when your body recognizes that it’s been infected by a virus, the immune system is activated. Sometimes, the first symptom people experience with a cold is a sore throat because the tonsils go into overdrive when the immune system is activated.
Prevent a Cold
Always wash your hands (in soap and water or hand sanitizer). Touching your face can allow germs to enter your body but can spread your germs to other surfaces or people.
Learn to sneeze or cough into your elbows. It keeps the spray from getting on your hands or surfaces and items around you.
Use sanitizing wipes to clean surfaces you may touch regularly or that you know someone sick has touched.
Why don’t we vaccinate for the cold?
Vaccines are prioritized a few ways. We want to vaccinate against things that:
- kill people.
Colds don’t kill a lot people, they just make us miserable and miss work. - spread really fast.
Flu, measles, chicken pox all spread rapidly through the population due to droplet exposure. - have slow-changing characteristics.
There are 99 different version of the “cold” virus, but each one is fundamentally different. So you would have to get 99 vaccines!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
The Flu or an Imposter? [Show Notes]

5 other viruses that cause “flu” symptoms
- Rhinovirus (cold) – most colds don’t come with a high fever, but the other symptoms are present.
- Coronavirus (SARS) – includes gastritis, nausea, and vomiting on top of the other symptoms
- RSV – usually prominent in kids and leads to hospitalization due to the respiratory inflammation that can lead to an emergency
- Adenovirus – first isolated in the adenoids; responsible for viral tonsillitis
- Parainfluenza virus – in the 50’s, they would swab the mouth or throat to determine what was making a person sick. There was a group of kids sick with the “flu” symptoms. The doctors swabbed all these kids and noticed that some showed a virus that wasn’t the influenza virus they were used to seeing, so it’s name essentially means “around influenza”.
These viruses have nothing in their makeup similar to influenza, therefore, the flu shot will not protect you against these.
Are flu shots really worthwhile?
The short answer, yes. It not only keeps the shot-getter protected (and even a little protection is better than none at all), it keeps healthy people from being carriers of the virus from spreading it to weaker members of the population (little kids, elderly, immunocompromised). And while the flu isn’t the primary reason people end up hospitalized or dying, the secondary complications (i.e. pneumonia) are what can kill people. Getting the flu shot is a simple and quick process, and is also relatively painless.
And there is absolutely NOTHING in the flu shot that can give you the flu. Your body can have an immune response because that’s the point of the shot, to activate your immune system so it’ll learn what to do if the real flu shows up. But obviously there are 5 other viruses you can catch that will give you symptoms identical to the flu.
Do more people get sick now than a few years back?
More people on the planet means more people probably get sick. But if we have a preventable disease and people choose not to prevent it (in themselves or their kids), then more people will start getting it (aka measles). We had almost eradicated measles from the US until a larger group of people decided not to get their kids vaccinated, and now it has resurged. Children worldwide die from measles, why would we want to put our own kids at that risk?
Despite the poorly matched vaccine in recent years, those that got the flu reported shorter duration and milder symptoms.
And obviously, the flu shot is not the only thing that is going to protect you from the flu this winter.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Punctures and Cellulitis [Show Notes]

Puncture Wound
A wound that is deep but a small point of entry (i.e. nail). This allows the bacteria to get stuck inside. Thus it won’t always bleed cuz the opening is too small for it to make it out. So if the blood can’t get out, then antibiotic ointments can’t get in.
Signs of Infection
- Swelling
- Redness
- Pain
- Warm
- “Lumpy” or “Dimpled”
- Oozing
- “Running” or “crawling” veins
Lockjaw anyone? Tetanus is an opportunistic infection that gets into the body from dirty objects and then causes muscle rigidity (among other things). It is very easy to prevent with a booster shot.
Cellulitis is not the same as cellulite, but does affect the same layer of the skin! It’s an infection caused by the normal bacteria that live on your skin. As long as it’s on your skin – cool, we’re friends. If it gets in your skin – that’s trouble. Staph or strep – friends on the outside, enemies on the inside. Requires oral antibiotics, and sometimes, even IV antibiotics.
Necrotizing fasciitis – bacterial infection gets so deep into the skin layers that it starts eating away the dermis and muscles below it.
Risks for Cellulitis
- surgical sites
- cuts and abrasions
- puncture wounds!!!!
- skin ulcers (from prosthetics, wheelchairs, or being bedridden)
- spider and insect bites (bugs aren’t sterile, plus toxins – ick!)
- cracked dry skin
- hangnails
- athlete’s foot (skin changes, including cracking)
Takeaway
Puncture wounds should not be treated at home – especially if you were stuck by something dirty.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
“Fluffing a Duck” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Feed You Bones [Show Notes]
Basics
Calcium is a natural element (yep, one of those periodic table guys). Our teeth and our bones are made strong by it.
For most healthy adults, daily recommended amount is 1000 mg. For females approaching 50 years old, recommendation increases to 1200 mg to 15oo mg per day.
The trick to supplementation is knowing that your body can only absorb 500 mg of elemental calcium at a time. So you gotta split it up. When you get it from your diet, then this is NBD because it will naturally be spread out between your meals and snacks.
These supplements always go with Vitamin D. Vitamin D is responsible for helping with calcium absorption. If you’re low on D (and more people are than might realize b/c very few jobs have you working out in the sun – and Vitamin D is synthesized and activated by UV exposure), calcium can’t be absorbed and used like it should.
2 types of OTC supplements
- Calcium carbonate (Caltrate) – a base (also what makes up OTC antacid tablets [i.e. Tums] so a bonus if you have heartburn); requires the acid in your stomach to break out of the tablet for your body to use.
- Calcium citrate (Citracal) – an acid; doesn’t require extra stomach acid to be absorbed. A good supplement for those who had gastric bypass, because the stomach has been shrunk and there are less acid pumps to break down medications that require acid to work. Bad for people with reflux or ulcers.
The labels can be tricky. It will say “600 mg Calcium Carbonate”, but you have to look for the hint of how much elemental calcium that is equal to. This is because your recommended daily dose is in milligrams of elemental calcium. So, doctors don’t always tell you that when they recommend it. Your calcium-rich foods are going to provide you with 250-300 mg of elemental calcium per serving (about 25% of your daily requirement).
Random dietary sources (between 6-20% of your daily requirement)
- White Beans
- Black-eyed Peas
- Sardines (cuz you eat their bones?!)
- Dried Figs
- Bok Choy
- Molasses
- Kale
- Turnip Greens
- Almonds
- Oranges
- Sesame Seeds
Calcium-fortified foods
- Instant Oatmeal
- Mainstream orange juices
- Soy products (because you’re using them instead of dairy and animal products)
- Cheerios
Vitamin D helps your stomach absorb the calcium into the blood. And then in the blood, keeps the calcium from binding with other things, so it’s free when the body needs it in other places.
Unfortunately, pounding supplements is not going to reverse osteoporosis.
Recommended dose for kids
- 1 to 3 years old — 700 milligrams daily
- 4 to 8 years old — 1,000 milligrams daily
- 9 to 18 years old — 1,300 milligrams daily
Usually not hard for kids to get the right amount with their diet plus a vitamin. Babies don’t need supplementation since their main source of nutrition is milk (breast milk or formula).
Seasonal Affective Disorder – is partly due to a Vit D deficiency, because Vit D also helps with mood. The sun exposure is the best way to supply your body with Vit D. A bonus is that sunlight stimulates serotonin production in your brain which is also responsible for good mood.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Medication Disposal [Show Notes]

The Regulation
The FDA and EPA agree that certain medications are okay to flush. The comparison being, the medication, though diluted, are still being present in tap water after filtration and purification, or a kid or petor junkie eating it out of your trash and getting really hurt or dying.
This is usually the advice for extended release pain medications (tablets, liquids, or patches), narcotics, and other controlled substances.
Homemade Disposal
The goal of disposing medications at home is to make it unappetizing to anyone who may find it and try to eat it.
Ingredients: Unwanted medications, Water, Sand, Cat litter, or coffee grounds
Crush the tablets or capsules in a ziplock bag. Add water to dissolve. Add sand/cat litter/coffee grounds to absorb water. Throw in trash.
Available for purchase
If you don’t want to DIY at home, Medaway bags are available at a pharmacy. They have an activated charcoal compound in it. Add pills, add warm water, and shake. Adsorption = when one compound adheres to another compound and they can’t be separated.
Privacy Recommendations
It is advised to throw away the medications separate from the prescription bottle. Best option is to remove labels and shred with other personal information. At the very least, black out all of your personal information and the drug information before putting in the trash. Even if your bottle is empty, if someone finds a bottle that previously held pain pills, that person may think you have more and it puts you at higher risk for crime.
Syringes
For syringe disposal, you can buy Sharps containers at a pharmacy. All the instructions for using, and packing and shipping, including a prepaid return label, are included in the box. If you don’t use an official Sharps container, it’s best to use an opaque jug or carton that 1) you can’t see through to see the needles easily, and 2) that has a small opening so it’s difficult for the needles to come back out (either by someone reaching in for them or by spillage). Once it’s full, just seal it and put it in the trash (do not try to recycle that jug!).
National Prescription Drug Take-Back Day – local law enforcement agencies are set up to take back unused or unwanted medications from the public and will dispose of them properly. Only certain locations will take controlled substances (check the website for your zip).
Holla
“Stoned raccoons aren’t funny!” – @kendh
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Measuring [Show Notes]
Measuring Liquids
Medication for kids are usually in liquid form and require some kind of device to accurately measure the dose.
1 teaspoon = 5 ml
1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons = 15 ml
1 fl oz = 30 ml
Milliliters = ml = cc = cubic centimeters –> all the same
Kitchen spoons and cooking teaspoons are not accurately calibrated to measure medication.
My Home Experiment
100 mg/5 ml = 20 mg/ml
Incorrect spoon #1: 4 ml < 5 ml (80 mg < 100 mg)
Incorrect spoon #2: 3.5 ml < 5 ml (75 mg < 100 mg)
Incorrect spoon #3: 6 ml > 5 ml (120 mg > 100 mg)
The cups that come with liquid OTC medications are calibrated accurately to measure medication.
Restaurant spoons are HUGE sometimes.
The Results
Maximum error when testing kitchen spoons is a 40% error (meaning it could be 40% below or 40% above the standard of 5 ml in a teaspoon). For a 500 mg/5 ml medication – a 40% error is equal to 200 mg too much or 200 mg too few. That could mean the difference in not being treated adequately and leading to complications (i.e. infection resistance) or being over-treated and experiencing side effects.
It’s a different story if you’re taking an adult dose (i.e tablet, capsule – which is already pre-measured) and putting it into something more palatable.
History of pharmacy: the only way pharmacists got medicine to people was by mixing it up and making the pills themselves. The process of taking bulk ingredients and making specialized forms of medications is called compounding.
Brand to generic conversion: generics are only allowed to have a 5% variation from the brand name, and some companies are even more strict on themselves and follow a 3% error standard.
3% << 40%!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Medication Intolerances 3 [Show Notes]

Tidbits about Headaches
A headache is an ambiguous side effect because there are so many different things that can cause headaches. Hormones are a big culprit of this. Blood pressure medications can too.
For someone with chronic high blood pressure, the higher pressure becomes the body’s new “normal”. Once medication starts to bring it down, even though the pressures are within a normal range, the body will experience symptoms of low blood pressure.
2 lies people tell about allergies
- No allergies – so then they take something they are allergic to and have an emergency
- Allergic to “everything” – because they experienced mild or moderate side effects. Or in the case of pain pill seekers, they’re “allergic” to the weak pain meds to get the doctor to prescribe stronger ones.
Stimulants
Irritability, nervousness, jitteriness, or moodiness can be a side effect of amphetamines (used for ADD) or cold medicines (i.e. pseudoephedrine).
A factoid about ADD/ADHD: the focus and attention area of the brain are underactive, so a stimulant helps it be more active so improve focus.
The biggest complaint people have from any stimulant is the inability to sleep at night. Just need to make sure it’s taken early enough in the day so it wears off in time for bed.
Bones and Joints
In this case, we rarely want you to keep taking the medication if these side effects happen. For example, cholesterol medications (i.e. statins, and fibrates) and quinolone antibiotics (Levaquin, Cipro, Avelox). The quinolones have a rare but serious side effect of tendon rupture; it is painful and permanent.
Tendons: the connective tissue that anchors muscles to the bones.
Osteoporosis medications can lead to bone pain – since their job is to cause changes in the way the bones are built and rebuilt, it’s not uncommon to feel something. But usually temporary.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Medication Intolerances 2 [Show Notes]

3 drug intolerances that involve the skin
- Itching and rash – even though they are a big sign of allergies, they also can be typical side effects of medications
- Narcotics – in hospitals, they give diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to calm an itching side effect
- Sulfa antibiotics and tetracyclines – sun hypersensitivity. Not a sunburn, though. May require pain reliever to get comfortable.
- Flushing – redness and hotness of the skin
- Niacin – used for cholesterol reduction. Flushing is reduced by taking 81 mg of aspirin 30 minutes before taking niacin
- Hormones – natural or in medication (birth control or hormone replacement). Can be reduced or eased by taking before bed or taking with food
- IV contrast – as the medication spreads through the body.
- Dryness – especially of skin surfaces that require moisture (i.e. mucous membranes)
- Antihistamines and cold medications – dry eyes, dry nose
- Overactive bladder medications – dry eyes, dry mouth, constipation
- IBS meds that control diarrhea – constipation
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Medication Intolerances 1 [Show Notes]

Allergy vs Intolerance
Medication allergies, especially the dangerous, life-threatening kind, affect your entire body, multiple organ systems, and put you at serious risk of death. They also require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms include:
- Serious swelling
- Not being able to breathe or swallow
- Significant speeding or slowing of your heart rate or breathing
- Blood leaking out of blood vessels into other regions of your body
Intolerances are usually related to regular side effects of the medications, but are so bad that you can’t tolerate it. At no time should you be asked to keep taking something that makes you feel worse than death. And in most cases, avoid it at all costs. Other times, the discomfort can be short-lived or fixed by altering how the medication is used.
My main point is: intolerances to medication side effects are not true allergies (even though a lot of people will group them together when giving a medical history to a doctor or pharmacy).
Nausea
Nausea is a side effect of almost everything that you swallow. It’s too vague and nondescript to be an allergy. It is usually due to the increase in acid production by the stomach when it is trying to break down and dissolve the medication.
Nausea can be caused by:
- Pain medications (narcotics)
- Antibiotics
- Any large, powdery elephant-sized tablet
- Multivitamins
Nausea is a potential side effect of almost everything that you swallow. It’s too vague and nondescript to be an allergy. It is usually due to the increase in acid production by the stomach when it is trying to break down and dissolve the medication.
The main way to avoid nausea is to take the medication with food – and in some cases, a decent amount of food.
Some widespread advice is to take medications with milk because milk is a base to counteract the stomach acid. Unfortunately, the calcium in milk and cause certain antibiotics to not work. Also, some medications require acid to be activated, so making the stomach less acidic, reduces their effectiveness.
A Positive Side of Nausea?
Certain injectable medications for Type 2 Diabetes have a main side effect of nausea or indigestion. With these medications, the patients are encouraged to keep taking them. The logic behind this is that in most cases, someone with Type 2 Diabetes will be overweight. And they may have been resistant to the lifestyle changes (i.e. diet and exercise) that would help improve their weight, thus also improving the diabetes outcomes. So, if they take a medication that causes nausea thus reducing their appetite, it helps them limit their food intake, and the final results will most likely be weight loss. This is really what the manufacturers think!
Diarrhea
Diarrhea can be caused by:
- Antibiotics: They kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but also your good bacteria.
- Take probiotics or eat live culture yogurt (the more diverse the better)
- Certain cholesterol medications: Particularly, the ones that help trap up the fat in your intestines so it’s not absorbed and add it to your waste that is about to exit. Fat is an oil. Oil is slippery. Poo that is slippery…you get the idea.
- The less fat you eat, the less slippery things will be.
- Metformin: It causes diarrhea in the beginning while the body is adjusting to it. Diarrhea lasting a month sounds like forever, but is really not compared to the amount of time (aka the rest of your life) that someone may have to take this medication for Type 2 Diabetes.
- The best way to control this is to start this medication low and slow.
The best way to counteract long-term diarrhea issues from medications is to use bulking fiber. They help absorb extra water and add solid substance to stool so it’s firmer.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Sleep Aids [Show Notes]

Who needs help falling asleep? *raises hand*
WARNING: Do not mix any sleep aids with alcohol – compounded drowsiness, depressed breathing or depressed heart rate
Sleep Aids
- Melatonin – the chemical your brain makes when it’s dark. Electronic light can interfere with your natural production of melatonin after the sun goes down.
- Valerian Root – claims to promote calming and relaxation
- 1st Generation Antihistamines – Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or Doxylamine (Unisom; also in NyQuil). They have natural drowsy side effect, so using for the purpose of that side effect is a common practice.
- Rozerem – stimulates melatonin production in your brain
- Hypnotics – Ambien (zolpidem), Lunesta (eszopiclone). They seduce your brain to sleep in an unnatural way, thus they have high risk side effects (vivid dreams, sleep driving/walking/eating) and a high risk of dependence. The side effects are due to the fact that the medications may get you to a deeper level of sleep before the rest of your body is prepared. Your body has a natural paralysis process to ensure you don’t act out dreams in the REM cycle, but if your brain reaches REM before your body is paralyzed, you may do crazy things!
- Benzodiazepines – generic names end in -lam or -pam. Also have a risk of dependence and side effects (mainly “hangover” effect).
- Tricyclic Antidepressants – a symptom of depression is sleeping too much, but insomnia can be a symptom of depression. Also, insomnia can make you feel depressed – it’s a vicious cycle. In small doses, they work to help rebalance the brain chemicals and reset the sleep-wake cycle.
Where to Start
Use as natural a solution as possible that is effective. Physiological and neurological issues can lead to chronic insomnia that is not corrected by the most natural solutions, thus pharmaceuticals are needed – and that’s nothing to be ashamed of!
Sunlight stimulates your eyes and tells your brain to make serotonin. When the light is gone, and that stimulation stops, serotonin stops and melatonin replaces it. This is how we functioned and planned our days back in the “old days”.
Summertime brings on long days and lots of sunlight. Thus we may not sleep as long because the long daylight hours keep us awake. But this can also be the issue in the winter and for people who experience SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) – the shorter daylight doesn’t allow sufficient serotonin to be produced and we actually feel sad.
Analyzing your sleep patterns and knowing your options will allow you to have a productive conversation with your doctor – different medications are used depending on if you have trouble falling asleep or waking up halfway through sleep or both.
Audience Question
*Melatonin in nursing: your natural melatonin gets in breast milk and is thought to help baby’s sleep cycle (especially early on when baby’s sleep-wake cycle may be backwards because that’s how they rolled in the womb). Thus, if your natural melatonin gets into breast milk, then supplemented melatonin will get there too. The rationale is that if you’re not sleeping (despite the exhaustion of having a new baby), then you may not be making enough natural melatonin. If you’re going to take melatonin while breastfeeding, LOW dose is key to ensure the excess isn’t deposited in the breast milk to pass on to baby – 3 mg seems to be the highest recommended, and I agree. PLEASE do your own research and discuss it with a medical professional you trust rather than just taking my word for it!*
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Sleep Hygiene

A Definition
Sleep Hygiene: how conducive your night time and bedtime habits are for restful sleep on a regular basis
Your body performs important processes while you sleep.
Risk of disease is increased when you don’t get enough sleep. Heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, just to name a few.
4 Areas of Sleep Hygiene
- Environment
- dark (all of our light-emitting toys are bad for our sleep) – your body makes serotonin stimulated by light, and then melatonin when the light is gone.
- temperature – your body sleeps well when it’s cool, kind of like hibernation. Gotta get past REM sleep because REM sleep is not restful sleep
- Habits
- no naps – recovery processes can be inefficient
- exercise (vigorous exercise during the day; slow & calming exercise late at night)
- getting adequate natural light – so your brain isn’t confused about which chemical it needs to make
- consistent routine – your brain likes predictable patterns
- Consumption
- stimulants – caffeine, nicotine
- alcohol – initially makes you sleepy, but can disrupt sleep when the liver finishes processing it into sugar
- large meals – can cause indigestion which can disrupt sleep
- drastic dietary changes – fluctuating amounts of sugar in the blood stream or digestive discomfort
- Mindset
- bed is for sleep – not a place for work or studying or eating
- avoid emotional stress – positive (i.e. excitement) or negative (i.e. anger)
Tidbits
CPAP machine – helps in sleep apnea, which is wear the body doesn’t get enough oxygen during sleep. Oxygen is needed for all sorts of processes. If the body can’t get the oxygen, then it probably isn’t using the nutrients and energy sources available, and it can lead to feeling awful, even after a night of sleep.
Nothing good comes from a lack of sleep.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Thrive with sleep [Show Notes]

3 Areas Thrive When You Sleep
1. Productivity
- Memory
- Attention span
- Creativity
2. Health
- Decreased risk for cardiac disease
- Inflammatory chemicals are cleansed out
- Weight management – certain metabolism processes only happen while you’re sleeping
- Tissues heal and rebuild
- Reaction time improves
3. Emotions
- Stress hormones are removed from your system
- Gives your serotonin production a break, so you get a fresh supply in the morning (Serotonin is your happy chemical)
The Bottom Line
The cells in your brain (neurons) run on electricity (aka the flow of positive and negative charges). Sleep allows the electricity to reset, so it’s really to flow quickly and efficiently the next morning. You live longer when you get enough sleep.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Know your body, love yourself [Show Notes]

Three ways to love yourself
1. Know how your body works and how to know when something goes wrong
2. If you have a chronic disease, know the ins and outs of it
2b.Finding friends or a community to support you
3. Do research about the decisions that you make, don’t just trust ads and fads
4*. Choose a healthcare team that is willing to listen to you and work with you instead of just working on you.
*Bonus!
No matter what method you choose to enhance your health, my goal is for you to be empowered with knowledge and confidence to make a decision you’re happy with, and not be bullied into doing something you don’t want to do.
Just remember, we will not find you in a textbook!
Holla
Yes, and I brag on @RachelCMayo – again! Because, well, she’s AWESOME!
#BoPoTribe stands for Body Positivity, where we believe all bodies are beautiful bodies. Founded by Susie @BeautyWithPlus
You can find the supportive community on Facebook, follow them on Twitter and Periscope, @bopotribe.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Special Episode #1: Interview with Rachel Mayo

Hemoglobin A1C
This test measures the percentage of your hemoglobin (the protein in your red blood cells that carry oxygen) has been coated in glucose. When there’s a lot of extra sugar floating around, it tends to stick to the other things floating around with it. Red blood cells live for 120 days*, so that’s a lot of time to let sugar hitch a ride. And while a blood glucose measurement gives a snapshot of what the blood sugar level is right now, the A1c measurements gives us an idea of what the blood sugar level has been during all the times you’re not pricking your finger to measure over the last 3 months*.
*I do realize that 120 days equals 4 months and not 3 months, but the really old and decrepit RBC’s that are close to their expiration are exactly that – decrepit, so they’re not in good enough shape to give us a trustworthy measurement.
Goal
For those with diabetes, the goal is to have an A1c >7%. For the average non-diabetic, A1c is ~ 5% (though with the American lifestyle, that “normal” number is creeping up – but that has more to do with Type 2 Diabetes).
Rachel received lots of support through the people she met through the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF) and continues to support their cause and actively helps other T1D’s get connected. She also participates in her local chapter of JDRF and participates in the Annual One Walk in Nashville (that’s where I got to hang out with Rachel for this interview!) You can find out what JDRF is all about by visiting JDRF.org and walk.JDRF.com.
++Time Sensitive ++ —> Follow Rachel on social media during the month of November to catch her Diabetes education Periscopes.

Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: “Radio Martini” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Insulin is not bad [Show Notes]

The Bottom Line
Without insulin, you would die!
Some Basics
Sugar scrub = sugar + water (+/- essential oils)
– a good exfoliant to remove dead skin
Your tiniest capillaries are so small that red blood cells can barely squeeze through one at a time. So, if the fluid around the red blood cell is full of sugar, it’s like that sugar scrub on your skin.
And that extra sugar can damage the capillaries in your eyes, finger tips, toes, and organs.
The cells in your body require glucose to do their jobs.
Insulin
Insulin is the only key that will let the glucose in. No key means no glucose. No glucose means no energy. And no energy eventually means death.
Insulin is also responsible for fat storage.
If you don’t eat the sugars, the body will use the fat stores on your body for energy. But if you don’t consume energy sources (by being on a specific diet) AND your energy stores are depleted, your body will break down the proteins (aka muscles of your body) to make energy. Your brain (and other organs in your body don’t want you to die).
Sugars and fats you eat gets turned into glucose. Insulin opens the doors to allow the cells to use the glucose. If there’s extra glucose around, insulin tells the liver to link it together to form glycogen and store it for later. If the glycogen storage is full, insulin tells the liver to turn the glucose into triglycerides (think clogged arteries and growing fat deposits).
Free glucose is the easiest and fastest to use. But during times that you’re not actively consuming sugars (like when you’re sleeping), your body is still working and that’s when glycogen can be used to provide glucose.
How much sugar in a day?
It’s always different for different people. The goal is having a level blood sugar as much of the day as possible. The rule of complex carbs being better than simple carbs is true, because it takes your body longer to break down and use complex carbs. While simple carbs usually dump a whole log of glucose in your blood stream at one time. And natural sugars are better than processed sugars because processed sugars tend to be more concentrated.
Your body has an easier time utilizing nutrients and supplements that look more like itself over ones that are synthesized in lab.
Holla!
Rachel Mayo is my diabetes hero!
Find her at:
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Boy Buys Vaginal Cream [Show Notes]

Basics
Yeast infection = fungal infection
Miconazole = -azole antifungal
Miconazole = Monistat
Yeast, or fungus, can affect any part of your skin.
Take Away
The medicine in the tube doesn’t care what body part you put it on, but the product manufacturer’s try to convince you that it does by changing the labeling on the package.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #6: Immunity [Show Notes]

Let’s Review
Liver contributes to:
1. Digesting your food
2. Metabolizing the energy from your food
3. Storage of Vitamins
4. Detoxing waste and toxins from your blood
5. Production of factors involved in blood clotting
Lastly, your liver keeps your healthy by aiding your immune system.
This is the last time we get to see this guy! *sad*
Sinusoids of Immunity
The last part of the lobule to be discussed is the sinusoids. Sinuses and sinusoids describe the space between (think about the sinuses in your your face – they are actually just holes and tubes through the bones of your face and skull that allow for empty space).
Sinusoids are lined with Kupffer cells (actually pronounced “Coop-fur”; I said it wrong on the broadcast – blame it on the accent). Kupffer cells are a part of your immune system (remember that your immune cells flow through the lymph system that parallels your blood vessels). Some of the cells involved in your immune system are called macrophages (big eater). When they find something that’s not supposed to be there, they gobble it up and carry it off to be disposed of or dissolve it into it’s basic parts and makes it safe.
Summary
Kupffer cells are macrophages that are stationed in the sinusoids of your lobules of your liver.
So, if you’ve had an infection and you start to get better, where do all the dead bacteria go? They end up floating around in your blood and the Kupffer cells will gobble them up. Kuppfer cells will do this for bacteria, fungi, and micro-parasites that they encounter. They also gobble up dead red blood cells and get them out of circulation. Other types of cells in your body die periodically and they, too, get gobbled up by Kupffer cells and have their parts recycled.
Dying cells and bacteria can release toxins if you had to wait on them to break down and dissolve on your own.
The liver is very efficient at all the things it does. Without your liver, processes that help your body thrive would take too long for you to reap the benefits.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #5: Production [Show Notes]

Basics
Most of the liver’s jobs have to do with taking things away from your blood supply or taking them apart.
Your liver produces 3 important components found in your blood. Two of them are involved in helping your blood clot. The third is involved in keeping your blood watery.
Prothrombin
The prefix “pro-“ means “starter” or “before”. Like “prologue” or “prodrugs”. In medicine, it usually means that it’s the starter piece but something has to happen to it (metabolism) for it to become useable.
Not Prozac…brand names of medications are developed by highly paid branding and marketing professionals.
Prothrombin gets activated into Thrombin when your body gets hurt and sends a signal that it needs help to stop the bleeding.
Fibrinogen
The suffix “-gen” means “creating” or “starter”. Fibrinogen gets activated into Fibrin.
So…. you get cut…. *ouch*
“I’m bleeding!”
The clotting cascade starts (way too complicated for this discussion).
When it gets to clotting factor X (ten).
CF X activates Prothrombin into Thrombin
Thrombin activates Fibrinogen into Fibrin
Fibrin – sounds like “fiber”. Fibrin is a protein. Some proteins are globular proteins – they are balled up in globs. Fibrous proteins are nice and stringy like fibers. So, Fibrin is fibrous.
Fibrin lays down a matrix over the wound and then the platelets that are floating around in your blood collect on the Fibrin and plugs the hole.
You want the blood in your body to stay liquid. You need the blood flowing out of your body to harden and stop.
Albumin (also found in the white parts of eggs).
It helps maintain the watery-ness of your blood. They maintain the osmotic pressure of your blood (there’s a big enough difference from the inside of a cell and the outside of the cell to allow the fluid to push through the membrane without needing a portal). If the pressure on both sides is the same, nutrients and chemicals will not transfer.
Albumin also helps the blood stay isotonic (same saltiness). You don’t want the fluid in your blood to be more salty than the fluid in your cells because the water will flow out of the cells into the blood to try and dilute it. But you don’t want the cells to be more salty either because the water will flow the other way and you won’t have enough liquid in your blood.
So, your liver takes the building blocks (amino acids) and puts them together to build these proteins.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #4: Detoxification [Show Notes]

100,000’s – get counting!

Enzymes
The hepatocytes contains enzymes. Enzymes are catalysts. While a lot of processes would probably happen naturally, they would be too slow to do us any good. Enzymes make those natural changes happen faster.
Think of an assembly line worker that does they same action over and over again on each piece being made. That’s how enzymes work.
Things that have floated around your body and done their job (i.e. drugs, hormones), the liver brings them back in and breaks them apart into inactive parts so they can be disposed of in one of your waste systems (urine or poo).
A lot of drugs go through the liver to become active and sent out to do a job, or to be deactivated after the job is done. You don’t want those things to stay around forever because they can become toxic.
Your liver also detoxes your body of used up hormones. Your body produces fresh ones as you need them, so the old ones need to be gotten rid of.
The most popular job that your liver does is filtering out alcohol. Science says an average liver can process 1 standard alcoholic drink per hour (for some people that’s longer – up to 4 hours).
Thus you have to be careful with cocktails and mixed drinks due to the different types of alcohol that get added together. 1 drink DOES NOT equal 1 glass!
Liver cleanses your blood of:
- Drugs
- Hormones
- Sex hormones
- Adrenaline
- Cortisol
- Alcohol
Thank your liver!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #3: Storage [Show Notes]

Recap
Digestion – bile breaks down fat to be absorbed by intestines
Metabolism – breaking down food into useful pieces
Your liver helps you store those energy sources until you need them – like times when you’re not eating.
Your body does lots of processes for you while you’re sleeping.
Storage
Glucose is a main source of energy for your body.
Insulin tells your cells to let glucose in the door so it can be used immediately. It also tells the liver to put extra glucose in long chains called Glycogen to store for future use.
Another energy source is fat or fatty acids. When the liver doesn’t have enough space for fat, it sends it to other areas of the body.
Certain vitamins (A, D, E, K) like to hang out in fat more than water, so it goes with the fat wherever it goes.
The liver stores Vitamin B12. B12 is usually promoted for energy boosting. A vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to a certain type of anemia (pernicious anemia). This means not enough red blood cells are being made, thus not enough oxygen is being delivered to all the parts of your body. Therefore your body doesn’t have the resources to utilize and create energy. End result: you feel tired.
Iron and copper are also stored by your liver until you need them. Low iron is another culprit of anemia.
Interesting fact: This is why liver tastes more metallic than other red meats.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #2: Metabolism [Show Notes]

Review
Liver – have one.
Lobule – yep!

Liver makes bile, helps digest fat in the intestines. Gallbladder? Holds bile until your intestines need bile.
3 main energy sources: Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins
Intestines absorb them into the blood and send them to the liver.
Basics of Metabolism
Metabolism = change
This type of change happens for 2 reasons:
- To make something useful
- To make something safe
What’s water got to do with it?
- Your blood is made of water
- Liver preforms hydrolysis on carbohydrates (using water to dissolve it into tiny bits of sugar = glucose)
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Glucose is the main form of sugar that your body uses for energy.
Sugars are the easiest to turn into energy so that gets used first. So low carb diets force the body to go after fats, which are the next easiest. If you’re eating low fat as well, then the body will burn the fat deposits on the body. Weight loss!
Fat Metabolism
The liver breaks down the fatty acids to make cholesterol (which is not always bad). Cholesterol is used in your cells walls to keep them fluid and slippery. Cholesterol is also used to make bile (think “like dissolves like”). If there’s any extra fatty acids the liver performs gluconeogenesis (gluco = glucose, neo = new, genesis = creation). It basically creating glucose out of anything that contains Carbon.
This is why fats are bad for Type 2 Diabetics as well as sugar.
Protein Metabolism
Protein is the hardest, but can still provide energy. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino = Nitrogen, acid = carbon. The nitrogen is relatively useless, so the liver turns it into urea, that gets sent out and filtered by the kidneys. The part with the carbon can be turned into glucose (gluconeogenesis again).
One of the intermediate steps of the urea production is ammonia. There is actually a blood test that can be done to test the ammonia-urea balance (BUN = Blood Urea Nitrogen), and if this is out of balance, it indicates a problem. This test may indicate that your body is metabolizing your own muscles. This can also be a sign of starvation or other nutritional imbalance. You need your muscles, you don’t want to metabolize your muscles.
Your body generally needs fully intact amino acids to build, rebuild, and heal muscles. Proteins and amino acids have a life span, so your body is constantly rebuilding and replacing with fresh supply. Athletes require higher protein diets than most because of this process.
Take Away
Glucose and fats aren’t inherently bad, it’s more about the amounts of each that get consumed and float around your body.
Your liver can be very efficient and metabolizing the foods you eat.
Your body gets fat deposits because the body is saturated with enough fatty acids that it needs, so any extra gets packed up and shipped around the body to be stored until later.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Liver Lesson #1: Digestion [Show Notes]

Review
Liver shaped like a triangle – check!
Lobule, hepatocytes, vessels – check! Hundreds of thousands – got it!

Bile Basics
Hepatocytes make bile.
It’s colors green due to red blood cell waste (bilirubin).
Bile consists of water, salt, cholesterol, bilirubin.
Bile moves from hepatocytes in liver to the gallbladder.
When you eat fats, the intestines triggers the gallbladder to send bile to help digest fat.
The fats are used in the energy-making process.
Bilirubin makes bile green. It also makes the skin yellow in jaundice. Makes poop brown.
For babies, it’s because baby hangs on to extra red blood cells from mommy after birth, and the liver has to learn what to do with all of them after they die (RBC’s only liver 120 days!). For adults with hepatitis, it’s because their liver is damaged and can’t work as efficiently as it used to. If your poop is the wrong color, it can indicate there is a major liver problem.
If you are gallbladderless, there is no where for the bile to be stored. So, it gets send to the intestines continuously. Also, if you have a meal heavy in fats, the intestines will just dump the food it can’t process faster towards the exit.
High levels of bilirubin in infants can lead to cerebral palsy. If the liver can’t handle all the bilirubin in a timely manner, the only other way to get it to breakdown is UV light.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
How to Hear Your Liver [Show Notes]

Liver Basics
Your liver is shaped like a lumpy triangle.
It is part of the digestive system, so having it close to the organs that carry your food means that blood doesn’t have to travel very far to get things to and from this organ.
During a physical exam, your doctor finds its location and size by percussing (aka tapping on it – just like a percussion instrument). Here is a video demonstrating the technique.
Microscopic Level
Hepatocytes (liver cells) build together into Lobules. Lobules build together into Lobes.

6 Functions
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Storage
- Detoxification
- Production
- Immunity
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
APAP vs NSAIDs
FAQ
APAP
NSAIDs
Bottom Line
Treating Injured Muscles [Show Notes]

How Muscles Work
Muscle contractions depend on the muscle cells trading Potassium (K⁺) and Calcium (Ca⁺⁺).
As your muscle uses up energy to do work, the by-product is Lactic Acid.
Muscle fibers are “woven” together – kinda like fabric.
Contracting and relaxing a muscle causes the fibers to grip together and then spread back out.
Bilateral muscles = symmetrical muscles. They look the same on each side of your body and worktogether to move your body in both directions from your center (left and right).
How Muscles Get Hurt
Stretching a muscle causes the muscle fibers to extend.
Over-extending a muscle can lead to a strain or pull/torn muscle.
Inflammation happens in the tiny fibers of your injured muscle.
Treatment Options for Injured Muscle
Anti-inflammatory medications work great for strained muscles.
– Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
– Naproxen (Aleve)
R.I.C.E.
Rest: stop using it, or at least give it a little break with only light use
Ice: yep, that cold, frozen water stuff
Compression: for smaller muscles, they can be wrapped to help limit inflammation and hold muscle fibers in a inoffensive position.
Elevation: smaller muscles that can be affected by gravity pulling blood to it, can benefit from being elevated and allowing gravity to pull blood away from it for a short time.
Here’s a link with a concise explanation of when to use ice vs when to use heat.
Prescription steroids help relieve inflammation.
Prescription muscle relaxers keep the muscle from knotting up.
Holla
@_KevinBuchanan used 800 mg ibuprofen for his injury. 800 mg should be taken every 8-12 hours, no sooner, or GI side effects may occur.
Recap
1. Stop the offending activity.
2. Ice the injured muscle (24-72 hours after injury)
3. Take anti-inflammatory pain relievers.
4. Apply heat to keep muscle relaxed
5. Gentle use or stretches
Behind the Scenes

Since baby sister was born, Jossalynn gets one-on-one time with me by riding in the “backpack”, which is a woven wrap by Pavo Form.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Cleaning Up Bacteria’s Mess [Show Notes]
Bacteria and Antibiotics
MIC stands for Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, and is the lowest amount of antibiotic required to stop the bacteria.
Antibiotics either kill the bacteria or slow it down enough that your own immune system can get rid of it.
Antibiotics are designed to keep a certain amount of medicine in your body over a certain number of days to ensure the infection is completely gone.
Do not take antibiotics that you have left over because you most likely do not have enough medicine for a full course of treatment.
Here’s a Metaphor
Think about a spot of dirt on the floor:
Dirt + a few drops of water = mud
Dirt + a whole pitcher of water = a watery mess
Dirt + a wet rag = clean floor
Relate it to Bacteria
Infection + too little antibiotic = resistance
Infection + too much antibiotic = side effects
Infection + the right dose of antibiotic = you get better
The Take Away
The gap between the lowest effective dose and the highest, non-toxic dose is called the Therapeutic Index. This is the information that is used to determine the dose of many medications and how they should be taken.
That is why you should always take antibiotics exactly as directed and until they are all gone.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Ear Wax Removal [Show Notes]

Ear Wax Basics
Ear wax is produced by your ear to keep junk out and away from your ear drum – like a slimey booby-trap.
Allergens and other things that go in your ears (like water, especially dirty water, like lake water) causes the production of ear wax to increase to the point it can become a problem.
When you swim under water, the deeper you go, the harder the pressure of that water pushing down on you gets, including the pressure of the water pushing in your ear. This pressure can smoosh wax up against your eardrum.
A quick tip to get water out of your ear – use a capful of rubbing alcohol. Alcohol evaporates quickly at room temperature, so when it mixes with the tiny amount of water in your ear, it helps that water evaporate faster.
Three Steps Ear Wax Removal (or maybe four)
1. Debrox (Carbamide Peroxide) – This is an OTC drop that helps dissolve ear wax if you have ear wax buildup. It can also soften an impaction (glob of wax smooshed against ear drum).
2. Take a hot shower. Ear wax – just like other waxes – when it gets warm, it will soften.
3. Irrigation with an ear bulb
1. Fill sink up with comfortably warm water.
2. Fill bulb with water.
3. Point affected ear down towards sink.
4. Put tip of bulb in your ear.
5. Squeeze water into ear and let water and wax drain back out.
4. Use a capful of alcohol to dry water droplets left over (optional)
NO EAR CANDLES!!
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Allergy Attack

Allergy Basics
Seasonal allergies can lead to nasal congestion and throat irritation, eye irritation with itchiness or watery eyes, or asthma-like symptoms.
If you can’t breathe or swallow or see, call 911.
At first sign of allergic reaction, take Benadryl (diphenhydramine). It’s an antihistamine to counteract the histamines that are part of an allergic reaction.
Benadryl also comes as a topical. The other option is Cortisone (hydrocortisone) – a steroid. This can’t be used all over your body because it can soak all the way through your skin and get in your bloodstream, which would lead to systemic effects of steroids. If you need systemic effects, it’s best to get a steroid prescribed by a doctor.
Antihistamines
1st Generation: Benadryl – drowsy side effects, works fast but wears off fast.
2nd Generation: Claritin, Zyrtec, Allegra – all have generics, all OTC, just take 1 time a day.
Steroid nasal sprays are newly OTC – Flonase and Nasacort. Localized steroids in your sinus passages can help block the other chemicals involved in allergic reactions, not just histamines.
The only medication that requires a doctor’s prescription is Singulair – it works best for asthma-like reactions that is produced in the lungs.
Also, Albuterol inhalers can be used for people who have asthma-like symptoms to open the airways back up quickly.
Audience Question
Is poison ivy cumulative in your body? (from @steve_tessler)
When you come in contact with an allergen (poison ivy leaves), you body recognizes it as a “bad guy”. Once your body deals with the offender, it “remembers” poison ivy, so the next time you come in contact with it, your body’s systems can be more efficient at taking care of it (antibodies). A problem arises if your body does “too good” of a job or gets overzealous. This can lead to a more serious reaction or possibly anaphylaxis.
Poison ivy is typically a topical offender. It would require an unusual type of exposure (i.e. burning it and inhaling the smoke) for it to affect other systems of you body than just your skin.
Avoid poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and any other poisons if you can help it.
Note: I told a story on the live broadcast. Afterwards, I checked my facts and found out I told it wrong, so I cut it out. Here is the real story (to the best of my knowledge – I reserve the right to add or correct details as I learn the full story)…
True Story
My husband’s grandfather burned a pile of brush that included some poison ivy or poison oak. He ended up breathing in some of the smoke which allowed it to go through his lungs and even into his bloodstream. It obviously caused a terrible, widespread reaction. And he would have an allergic reaction every year after that at about the same time as the original reaction.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
The Lady Who Caught on Fire

Burns: Rule of Thumb
If total burned area is larger than a softball, get medical attention.
A Quick Physics Lesson
Heat is a result of increased energy. Energy likes to flow from places of high energy to places of low energy until it’s equaled out. So heat will flow from the hot thing to the cool thing until they are the same temperature. Because the temperature difference between the hot thing and your skin is so large, the heat transfers really quickly, to the point that the water in the cells evaporates and causes cell injury.
Burns can lead to dehydration due to the loss of moisture from that area. Burns can also lead to infection due to cell injury and possible broken skin from blisters.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Drink Your Water

Water for Life
Avoid becoming dehydrated. Drink water, lots of water. Eight 8 oz glasses of water a day, at least.
Your body is mostly water. If you end up in a deficit, heat sickness or heat stroke may ensue.
Drink room temperature water to be able to drink more and absorb more. Here’s a website that explains different situations in which you should drink water at different temperatures.
If you feel thirsty, you’re already at a deficit and needs to be corrected ASAP.
Make sure kids are drinking water and staying hydrated. And your pets too!
Temperature References
Water freezes at 32º F
Refrigerated water is between 35-45º F
Room temperature is between 68-78º F
Body temperature is 98.6º F
Your hot water heater is probably set somewhere between 110-140º F
Water boils at 212º F
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Stomach Acid Overview

Stomach Acid Basics
Stomach acid causes heartburn.
Long-term reflux problems leads to a GERD diagnosis.
Stomach acid has a pH of 2.
Low pH = acid; High pH = base
Stomach acid is Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Some Biochemistry
The molecules of the acid like to spend their time joining together and breaking apart. So by attaching to something else instead of each other is how it can be dangerous but also how it helps digest food quickly.
Your stomach is designed to hold this strong acid safely.
There are pumps in the cells of the lining of your stomach that produce the acid.
Proton pumps work kind of like a water wheel – they move protons from inside the cell to outside to the stomach cavity.
Hydrogen atoms are made up of 1 proton (positive charge) and 1 electron (negative charge). So if you take the electron away from hydrogen, you are left with a proton with a positive charge.
Another process that helps create acid in the stomach relies on histamines.
They are not quite the same as the histamines that you hear about in relation to allergies. But there is a particular type of histamine that is only in your stomach.
Acid-reducing Medications
There is a class of medications for reflux called Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI). These medications turn off the pumps so they pump less protons into the stomach.
The medications for the histamine process are called Histamine 2 Receptor Blocker (H2RB).
H2RB’s work faster than PPI’s. Just like you can take an antihistamine and it block histamines causing allergies in just a dose or two, H2RB’s can work as fast as one or two doses. That is why they are advertised to treat heartburn after you eat or to help prevent heartburn before you eat.
PPI’s take up to 2 weeks to reach maximum effect.
The third option for heartburn are your antacids. They are bases that go into your stomach acid and help neutralize it.
OTC Medications (by class)
Antacids: Tums, Rolaids, Maalox, Mylanta – fastest
H2RB’s: Pepcid, Zantac, Tagamet – all have generics, all OTC
Tagamet can have drug-drug interactions with other prescription medications, so caution is advised.
PPI’s: Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium – some generic, newly OTC – slowest
Cautions
The downside to having reflux medications available OTC and people having the opportunity to self-treat is if there are any cellular changes in your esophagus.
Your esophagus is not designed to be in contact with that level of acid. As those cells are injured, they eventually change and can become cancer.
Fun Tidbit
Just like the cells of your skin are epithelial cells and their job is to keep the inside things in and the outside things out. Your digestive tract is also lined with epithelial cells. So technically the food you eat doesn’t go inside your body, it just moves through this tract that is “outside turned in”.
Holla
@steve_tessler‘s question: After he eats, he coughs for 30 minutes, and sometimes sneezes. Is this considered GERD? Cannot eat nuts or seeds due to diverticulitis. If he sits and rests it doesn’t get so bad, but if he has to be active right after a meal, it is.
Recommendation: try a H2RB morning and night and see if it contains the acid after meals. The next option could be a slight food allergy, possibly gluten, so cutting out certain foods would be necessary.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Type 1 Diabetes vs Type 2 Diabetes

Diabetes Facts
All of the cells in your body depend on different forms of sugars to make energy (mostly glucose though).
Insulin works like a key to unlock the doors of the cells and let the sugar in to be used.
Adults get newly diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes too, it’s not just a childhood disease like a lot of marking will make you think.
Diabetes: Type 1 vs Type 2
Type 1 Diabetes: The pancreas (insulin factory) quits working or becomes dysfunctional.
Type 2 Diabetes: The key holes and the doors are broken or jammed and the insulin “key” won’t fit in them as well or at all. This is known as insulin resistance.
In Type 1, you have to import insulin (aka injections), because you can’t make your own insulin anymore, ever.
Insulin pumps (outside pancreas) give a continuous flow of insulin and can sense sugar levels. It tries to operate as much like a natural pancreas would.
In Type 2, the medications are being developed to encourage your body to use your natural insulin as best and as long as possible.
There are lots of ways to get in a door if they key won’t work, thus there are lots of different medications to help in Type 2.
Holla!
Shout out to Rachel Mayo (@rachelcmayo) for her inspiration for this topic and for her strength and courage to not be scared of #T1D.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Too Much Acetaminophen?

Why is this important
Studies have been done regarding deaths caused by Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose, and they are finding that kids and adults are dying from having too much medicine with just a little bit extra over the recommended dose. [This American Life did a whole episode on Tylenol overdose stories]
Acetaminophen Basics
APAP is processed by enzymes in your liver. They are like little boats that carry drugs from one place to the other and cause them to make changes so it can do it’s job when it gets to the other side. So, APAP rides in it’s own little boat, and the body then uses it to reduce pain or fever.
The problem is, if there’s more APAP than boats, other things start happening to it, and it becomes very toxic. It not only damages liver, it can damage the DNA of your body. The only way to get it back in order and bind it back up, is for you to receive other pharmaceuticals in a hospital.
Most likely, if someone has had too much APAP, it takes about 4 days for them to experience any symptoms, and therefore, it’s probably too late for them to receive help.
Excedrin Migraine = Acetaminophen (APAP), Aspirin (ASA), Caffeine
Take Aways
Please don’t take more APAP than recommended.
They changed the maximum dose allowed from 4000mg per day to 3000 mg per day.
Extra strength APAP: 500 mg/ tab (1-2 tabs q 6 h) —> 500 x 2 = 1000 mg —> 3 doses in a day (6 tablets)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) include Aspirin, Ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin), Naproxen (Aleve)
The Side effects of NSAIDs are much more instantaneous, so if you take too much, you will know right away and can back off.
Many prescription pain medications contain APAP too.
Maximum Doses
APAP: 3000mg in 24 h
Aspirin: 6500 mg in 24h
Ibuprofen: 3200mg in 24h
Naproxen: 1250 mg in 24 h
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Shoo the Poo

OTC Medications for Constipation
Stool softener (Colace = Docuasate) – it’s job is to go into your digestive tract and attract water to soften things up.
Laxative (Dulcolax = Bisocodyl) – increases peristalsis (natural, rhythmic wave-like movement of your intestinal muscles).
Constipation Basics
Constipation can be caused by either that rhythm slowing down or stuff being so hard that the natural rhythm can’t move it fast enough.
Stool softeners make things softer so the natural motion can move it out, laxatives make the natural wave motion wave faster.
The downside to a stool softener is that it might not work fast enough for some people.
The downside to laxatives is that they might cause cramping and pain, and actually lead to diarrhea.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio




