Tonsils – Episode 110
Tonsils Basics
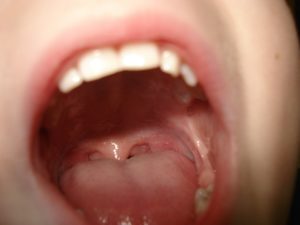
Your tonsils can be found in the back of your throat. You can open your mouth and look in the mirror and see them on each side of your mouth behind your teeth and tongue. You can also feel them below your earlobes and behind your jaw bone.
Tonsils are composed of lymph tissue since they are a part of your lymph system. They store white blood cells that help you fight off infection. Their activation during sickness is why they swell and get sore.
They are covered with the same mucosal membrane as the rest of the inside of your mouth. This mucosa layer has pits and crevices called crypts. These crypts increase the surface area of the mucosa that comes in contact with the lymph tissue and allows more opportunity for infectious material to be directly accessed by the immune system.
Infectious Tonsil Issues
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils. It can be classified as acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis is directly related to a viral or bacterial infection. Chronic tonsillitis can be either a persistent, long-lasting infection or multiple consecutive acute episodes that can appear to be one long sickness.
Swollen tonsils can cause simple activities such as swallowing, talking, and breathing very painful. You can see your swollen tonsils when you look in the mirror. They will appear red or possibly blistered.
Mono, an infection caused in adolescents and adults by the Epstein-Barr virus, cause severe swelling in all the lymph nodes, including the tonsils. This is one of the situations where your tonsils will be so inflamed, you can see the swelling on the outside of your face and neck. Because such a large portion of your lymph system is involved, including your spleen, this is a serious sickness.
Strep throat is probably the first infection you think about when you think of swollen tonsils. The bacteria, streptococcus, infect the lining of the tonsils and throat. This is why the doctor will swab your tonsils when they’re testing for strep.
Non-Infectious Tonsil Issues
A non-infectious reason the tonsils will be large is a condition caused hypertrophic tonsils. The tonsil tissue and/or mucosa overgrow and become oversized without any infection or immune activation being involved. Overgrown tonsil tissue can lead to snoring or sleep apnea, and that’s bad.
Another non-infectious issue with your tonsils is called tonsilloliths or tonsil stones. These stones happen when dead bacteria or food debris gets stuck in the crypts and they become calcified. They cause a sensation many describe as a crumb stuck in your throat. They can become quite large and can interfere with swallowing and eustachian tube function. Because the eustachian tubes run from your eardrum into your throat, if the tonsil is swollen enough, it may close off the tube to the ear and cause ear pressure/pain. Some tonsil stones are large enough to be visible and may have to be manually removed. Lastly, due to the composition of the stones (dead bacteria and old food), frequent tonsil stones can be the cause of bad breath.
There’s no way to prevent tonsil stones 100%. Good oral hygiene can certainly help reduce the frequency of stones, and can also help remove them quickly if they occur. The most common way of trying to remove a tonsil stone involve coughing, clearing your throat, or hissing. All three of these ways produce vibrations in the lining of the throat and mouth. So along with the exhalation of these methods, hopefully, the result is the stone coming out of the tonsil and out of your mouth.
PSA: Please DO NOT scratch your tonsils with your fingernails to remove a tonsil stone!
Callback
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
Music Credits: Up In My Jam (All Of A Sudden) by – Kubbi https://soundcloud.com/kubbiCreative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Music provided by Audio Library https://youtu.be/tDexBj46oNI