Liver Lesson #2: Metabolism [Show Notes]

Review
Liver – have one.
Lobule – yep!
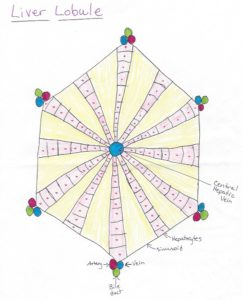
Liver makes bile, helps digest fat in the intestines. Gallbladder? Holds bile until your intestines need bile.
3 main energy sources: Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins
Intestines absorb them into the blood and send them to the liver.
Basics of Metabolism
Metabolism = change
This type of change happens for 2 reasons:
- To make something useful
- To make something safe
What’s water got to do with it?
- Your blood is made of water
- Liver preforms hydrolysis on carbohydrates (using water to dissolve it into tiny bits of sugar = glucose)
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Glucose is the main form of sugar that your body uses for energy.
Sugars are the easiest to turn into energy so that gets used first. So low carb diets force the body to go after fats, which are the next easiest. If you’re eating low fat as well, then the body will burn the fat deposits on the body. Weight loss!
Fat Metabolism
The liver breaks down the fatty acids to make cholesterol (which is not always bad). Cholesterol is used in your cells walls to keep them fluid and slippery. Cholesterol is also used to make bile (think “like dissolves like”). If there’s any extra fatty acids the liver performs gluconeogenesis (gluco = glucose, neo = new, genesis = creation). It basically creating glucose out of anything that contains Carbon.
This is why fats are bad for Type 2 Diabetics as well as sugar.
Protein Metabolism
Protein is the hardest, but can still provide energy. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino = Nitrogen, acid = carbon. The nitrogen is relatively useless, so the liver turns it into urea, that gets sent out and filtered by the kidneys. The part with the carbon can be turned into glucose (gluconeogenesis again).
One of the intermediate steps of the urea production is ammonia. There is actually a blood test that can be done to test the ammonia-urea balance (BUN = Blood Urea Nitrogen), and if this is out of balance, it indicates a problem. This test may indicate that your body is metabolizing your own muscles. This can also be a sign of starvation or other nutritional imbalance. You need your muscles, you don’t want to metabolize your muscles.
Your body generally needs fully intact amino acids to build, rebuild, and heal muscles. Proteins and amino acids have a life span, so your body is constantly rebuilding and replacing with fresh supply. Athletes require higher protein diets than most because of this process.
Take Away
Glucose and fats aren’t inherently bad, it’s more about the amounts of each that get consumed and float around your body.
Your liver can be very efficient and metabolizing the foods you eat.
Your body gets fat deposits because the body is saturated with enough fatty acids that it needs, so any extra gets packed up and shipped around the body to be stored until later.
Connect with me
Support us on Patreon
*NEW* Join the Pharmacist Answers Podcast Community on Facebook
Subscribe: iTunes, Stitcher, GooglePlay, TuneIn Radio
